Winter garden in a private house: 14 tips for arranging with your own hands + photo
Juicy greens and pleasant aromas of summer can be extended for the whole year. For this, winter gardens were invented. Just imagine how nice it will be in winter to go into a real garden under the roof and go back to the warm summers, breathe in the full smell of greenery and flowers, sit, relax, a couple of hours and have a great rest. Such a pleasure is worth a little confusion and organize a winter garden in a private house. On the way to your own oasis, you will have to solve a lot of issues, from the choice of place to the selection of plants. We will deal with the main aspects.
No. 1. Winter garden, greenhouse and greenhouse - what is the difference?
And a winter garden, and a greenhouse, and greenhouse Designed for growing plants. Everywhere you have to artificially create the necessary microclimate. So what is the difference and is it there? Roughly speaking, winter garden is created mainly for aesthetic pleasure person. The greenhouse and the greenhouse are focused on the cultivation of certain varieties of plants, and in the first place is the receipt of benefits.
The winter garden is usually adjacent to the house or located inside it. The greenhouse and the greenhouse are independent structures. Greenhouses are usually built temporarily, they are often used to grow certain crops at a particular stage. Greenhouses are used to grow exotic plants. A rather specific microclimate is created for them, in which a person is not very comfortable to be in.
In the winter garden it is comfortable for both man and plants. Greens are planted in order to please the eye. She will also have to create certain conditions. It is possible that you will even receive any kind of benefit, for example, from the cultivation of some flowers, but all this is a by-product. The main task of the winter garden is to give aesthetic pleasure, preserve the colors and aroma of summer, or even recreate a corner of overseas nature.
First winter gardens appeared in ancient Egypt. Then in the palaces the rich put stone vases with plants. The facts of using winter gardens in ancient Rome are confirmed. Then the greenery was placed on the windowsills, and the richest allocated a separate room for the garden in the house, decorating it with columns. Later, the idea of a indoor garden conquered Holland, France, England, and then the whole world. Today, winter gardens are at the peak of popularity. Of course, you can try and build a small likeness in an ordinary apartment, but the owner was much more lucky of their homes - you can turn around in them and realize almost any idea.
No. 2. The main types of winter gardens
Depending on location, functionality and role winter gardens can be of such types:
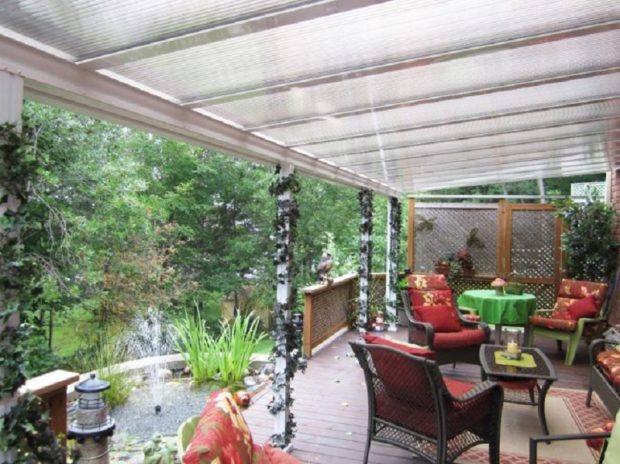
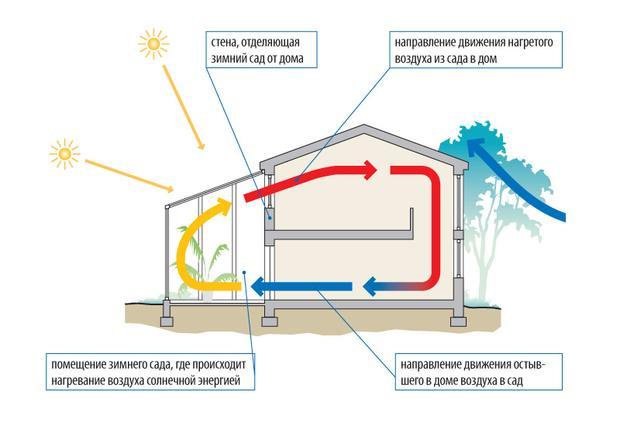
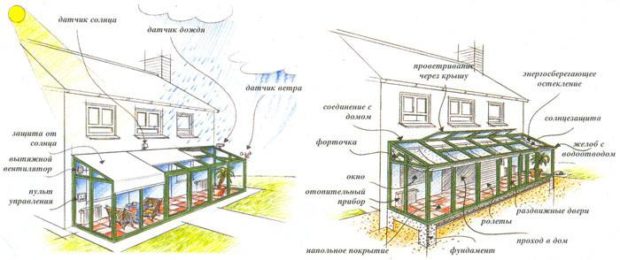
- buffer garden settles down in an extension to the house, most often on a verandah. This is the case when the "thermal trap" becomes an excellent place for breeding greenery and organizing a recreation area;

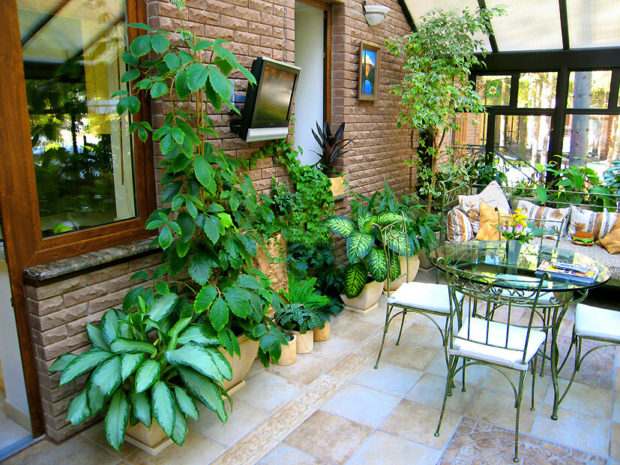
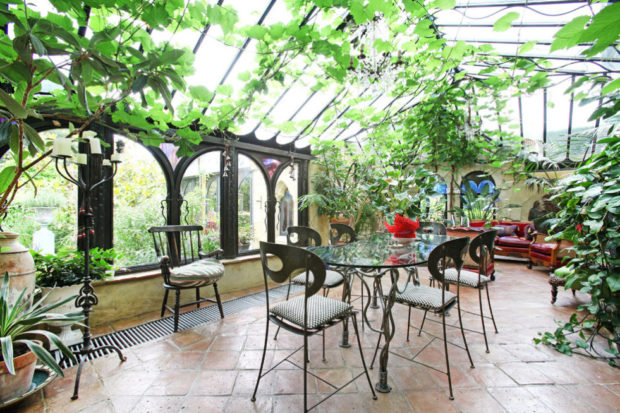
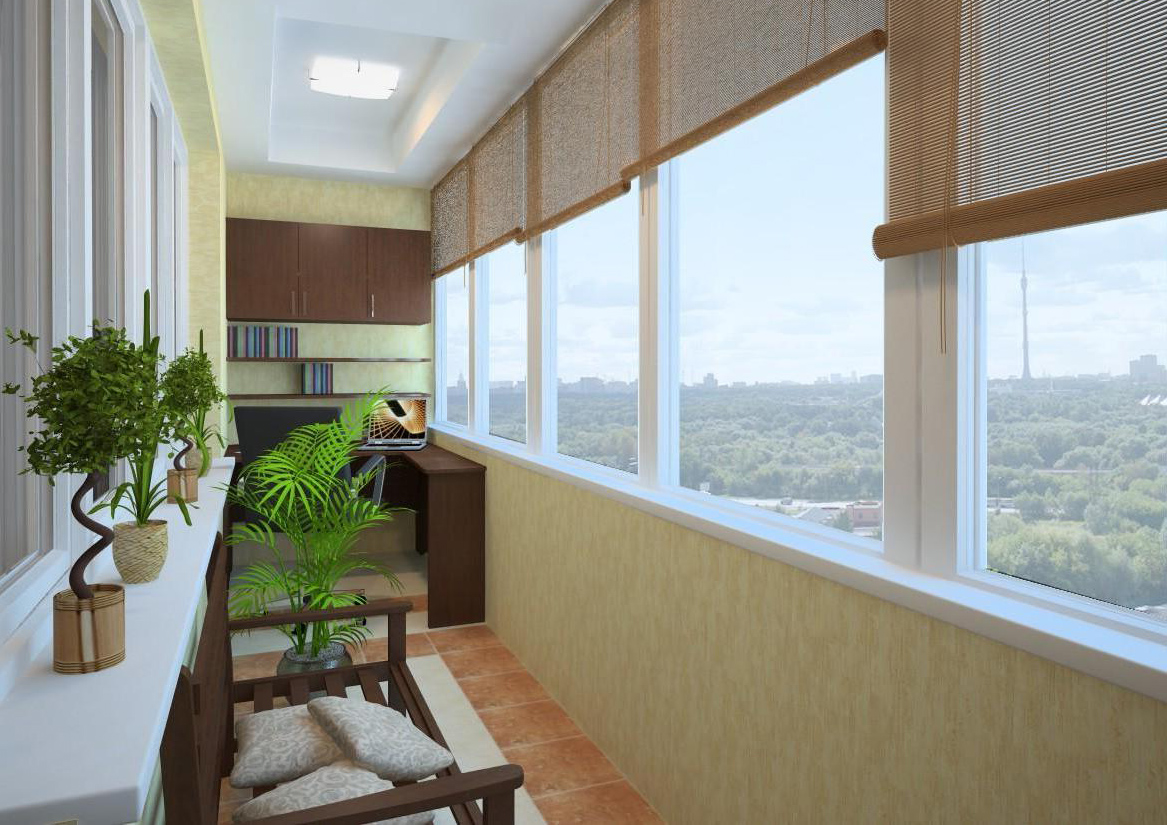
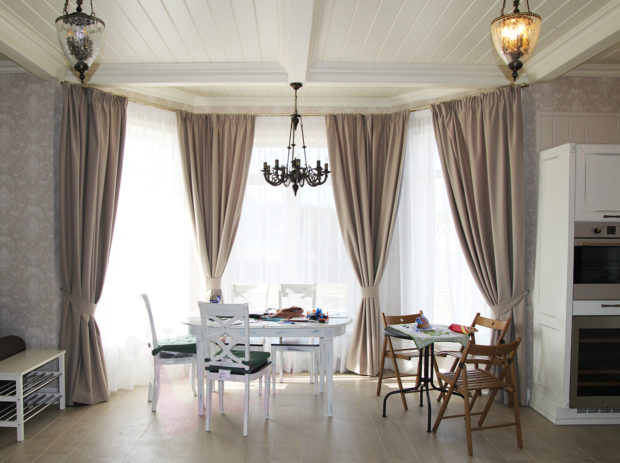
- residential winter garden fully or partially glazed, used as a full-fledged part of the living space.In such a room, in addition to plants, there is a living room, dining room or just a recreation area. Conditions are created that will be comfortable for both plants and humans;
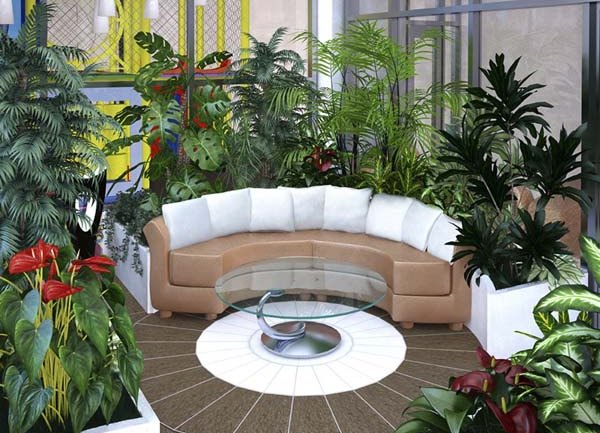
- conservatory conservatory - This is a non-residential premises in which optimal conditions are created for growing exotic plants. Unlike greenhouses, such varieties are grown here more for admiring than for profit. If the area allows, you can create a corner of tropical nature with ponds, alleys, recreation areas.

No. 3. Choosing the right place
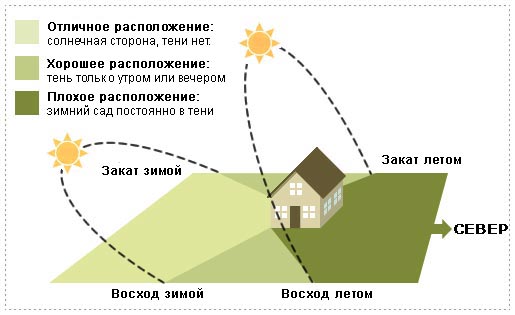
As a rule, a winter garden is organized in an extension to the house, and in this case it is very important which side this extension will be located on:
- east side is considered most preferred. Plants will receive maximum light and heat from the morning sun, but will not overheat;
- South side It shows its best side only in the winter, when heat and light are in short supply. In summer, the plants will overheat, so you have to work hard to provide them with sufficient watering, shading and ventilation;
- west side - a good solution, in such a garden the evening warmth will be kept for a long time, which is beneficial in winter conditions, but not very good in summer. Have to take more care of ventilation and watering;
- garden located from the north side, will quickly accumulate and give off heat. This is the least successful location, but if there is no other way, then you will have to provide a reliable heating and lighting system, choose plants that are more resistant to shade and low temperatures.

Very often converted to a winter garden verandasequipping them with the necessary engineering systems.
A much less common winter garden is located on the roof.. This is a technically more complex solution, it is necessary to calculate the load on the supporting structures, properly organize the roof, supply all communications. But in return you get a house that compares favorably with the rest. There will be no problems finding the side of the world, and households will be able to admire not only plants, but also the starry sky.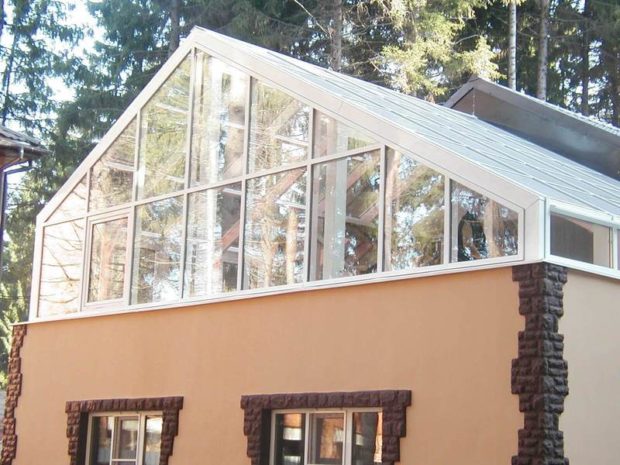
Number 4. Conservatory design
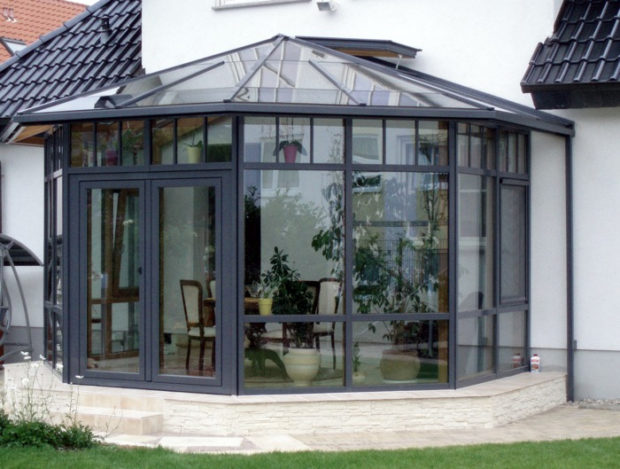
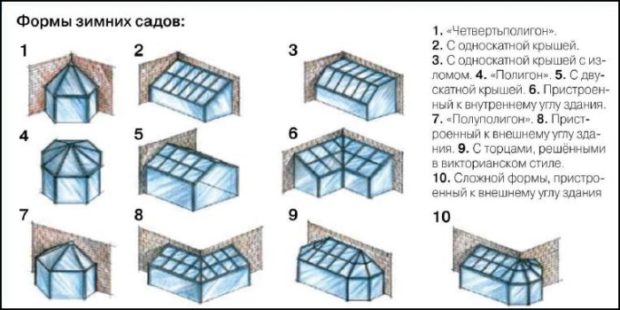
Winter garden can be realized as a separate buildingbut this option is rare. He usually adjoins the house, and in this case, the design may have different shape:
- rectangular with a pitched roof - the most common option, since it is simpler than the others in implementation;
- the design attached to the outer corner of the house allows you to arrange several groups of plants in the garden that require different conditions in terms of light and temperature;
- a structure attached to the inner corner of the house with a three-pitched roof protects plants from negative environmental factors. Suitable for delicate, heat-loving varieties. An L-shaped structure can be attached to the inner corner;
- an extension with a gable and four-beam roof looks more interesting and allows you to let in more sunlight;
- rectangular extension with a pitched roof and an expanded roofing part;
- bay windows structures become a logical continuation of the residential area.

No. 5. Optimal material for the winter garden
To ensure that the plants receive a sufficient amount of sunlight and heat, it is necessary to make the design of the winter garden as accessible as possible to the light. Both walls and roofs are best made from transparent materials. The most popular are:
- glass used for many years to equip not only winter gardens, but also greenhouses and greenhouses. It is highly durable, withstands snow and wind loads, transmits 98% of the rays, and allows the space inside the garden to quickly warm up. However, with a strong impact, the glass can break, the material is expensive, it is difficult to process. To save money, many go to reduce the thickness of the glass, but at the same time it will be necessary to strengthen the frame (part of the light is stolen), and thin glass will keep the heat even worse than the standard one;

- polycarbonate lighter than glass, cheaper, easier to process. The material can be bent, it is fully moisture resistant, not afraid of corrosion and fungus. However, in terms of light transmission, it is inferior to glass - it transmits only about 88% of the rays. Moreover, it cannot boast of high heat efficiency, so a serious heating system will be needed;

- double-glazed windows They cost a lot and weigh decently, but they store heat well inside the garden, and by light transmission they stand in one place with glass. If you choose not ordinary glasses, but energy-saving ones, you will be able to decently save on heat, and that is why today double-glazed windows are used increasingly in the arrangement of winter gardens;

- plexiglass usually used in combination with other material to equip the side walls. The material is perfect for these purposes, but has a large weight.
No. 6. Foundation and frame
So that the winter garden does not sag, it is better to take care of the construction solid foundation. This is a rather time-consuming and costly part of the entire project - it takes about a fifth of the budget to create the foundation. Will fit shallow strip foundation. You can use ready-made reinforced or reinforced concrete blocks with a thickness of 20 cm to create it. Depth depends on the type of soil, climate and topography. Instead of ready-made blocks, you can use concrete mortarbut you have to work hard with the formwork and reinforcement cage.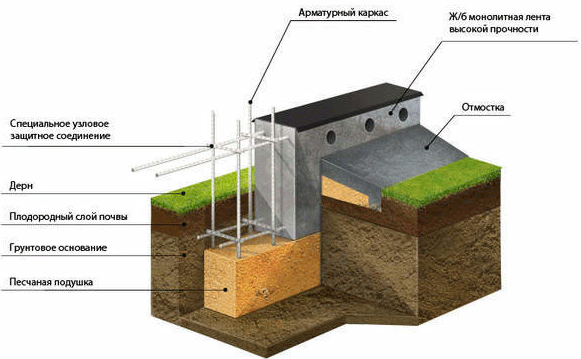
The floor is made of concrete, then it can be faced ceramic tiles, natural or artificial stone, porcelain stoneware or terrace board. The board is also used, but less frequently.
For the arrangement of the frame, you can use ready-made structures, for example, aluminum or steel profile, wood. You can go the more difficult way and build the frame yourself. It goes brickas well as all the same wood, aluminum and steel. After mounting the frame, glazing is started with the selected material.
When equipping the roof, do not forget to provide a slope so that in winter the snow does not linger on the roof, does not increase the load and does not block sunlight.
Number 7. Choosing a heating system
Choosing the right place and material for glazing is only half the story. Of course, plants will receive a large amount of heat from the sun, but in winter this may not be enough, so even at the design stage they select the most optimal heating system. The choice depends on the area, type of plants grown and even from the regularity of visiting the garden. If frost-resistant plants are planted, and you are not in the garden every day, you can do heater. If the garden is part of a permanently inhabited house, then it is necessary to think over a more serious heating system.
To choose today is from:
- electric heaters do not require complex installation, they can be moved from place to place, they allow you to quickly heat the room and quickly adjust the amount of heat. Such heaters cost democratically, but are expensive to operate, especially if you use them regularly and heat a large area. Another problem is air drying;

- water heating, i.e. connecting the garden to the heating system of the house with installation radiators. As a result, it turns out to achieve stable temperatures, the costs will be minimal, and the microclimate in all areas of the house will be the same. Minus - the complexity of the arrangement. It is better to plan such a heating system at the stage building a house and summing up all communications. In order to correctly insert it later, you will need calculations and the help of specialists, and even then not always, it will be possible;
- warm floor (water or electric) allows you to optimally warm the room. Soil and water for irrigation will be heated first. If you correctly lay the cable or pipes, the walls of the garden will also warm up, which will prevent their icing. The disadvantages include the cost of this method.It will be difficult to repair the water system, its arrangement is a complex process. Electric underfloor heating is easier to organize, but the cost of maintaining it will be higher;

- split systems do not dry the air, allow you to quickly warm up the room, quickly adjust the temperature, but are not suitable for regions with low winter temperatures;
- Ural Federal District do not dry air, heat surfaces, not air, i.e. acting on the principle of the sun. For a compact winter garden - that’s it, but for a large room this is not an option;
- stove heating allows you to get cheap heat, but it will be distributed unevenly, which is not good for plants, and you will have to constantly throw firewood / coal - leave it without a person such an oven dangerously;
- air heating allows you to use warm air from living quarters. He through the windows and fans distilled into the garden. It turns out cheaply, but the whole system takes up a lot of space, and the appearance of the garden will be spoiled by the duct system.
Several systems can be combined.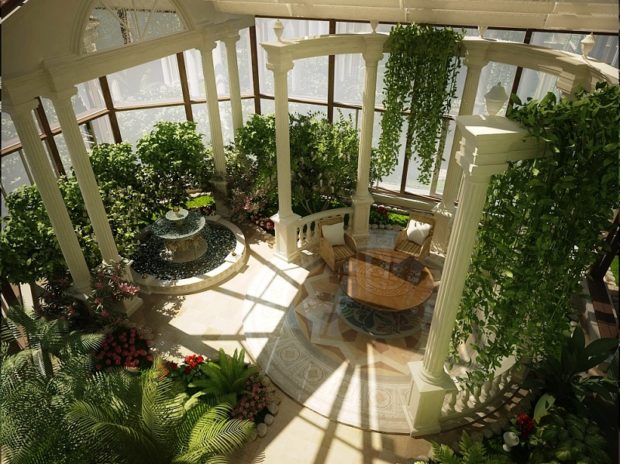
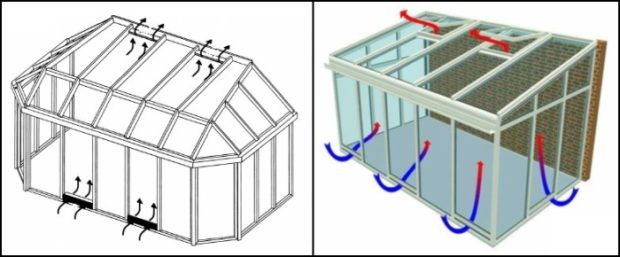
Number 8. Choosing a ventilation system
Plants need an influx of fresh air - this is the key to their normal life. It is necessary to provide for the path of air from the street to the garden, as well as air exhaust from the garden. There are only two options:
- natural ventilation It is equipped due to the presence of window leaves and transoms for fresh air. Exhaust air escapes through special openings or valves at the top. The air flow can be adjusted by opening and closing the windows. A minimum of investments and a minimum of noise, but normal ventilation is provided only if there is a difference in temperature outside and inside. So that the valves do not damage the plants, and do not obscure them, it is better to provide a sliding mechanism for opening them. Also do not forget about mosquito nets;

- mechanical ventilation will work even in the absence of wind and the necessary temperature difference. It differs from the natural one in that the outflow of air is carried out using fans. Sometimes even more complex systems are used, where inflow and outflow are forced. The microclimate will be fine, but your relaxation in such a garden can be overshadowed by the noise of the working fans. In addition, these are additional expenses for installation, electricity and periodic maintenance.

No. 9. Winter garden lighting system
A winter garden in a private house needs artificial light, because in winter, sunlight may not be enough for the normal growth and development of greenery. Will have to take care of wiring and study the light spectrum of different types of lamps to choose the right ones. To ensure photosynthesis, it is necessary that the lamp gives rays in the range 400-500 nm (blue spectrum), 500-600 nm (green, for photosynthesis of the lower leaves), 600-700 nm (red). Light 1200-1600 nm accelerates many biochemical reactions.
- Incandescent lamps (rays of the spectrum of 600 nm) give too much heat, can burn high plants, and in their spectrum there is no blue spectrum necessary for photosynthesis.
- Fluorescent lamps perfectly cope with the requirements put forward, but they are dimensional and suffer greatly from voltage surges.
- High Pressure Sodium Lamps economical, usually used in large greenhouses, difficult to install, require the installation of additional equipment.
- Mercury lamps high-pressure systems are inexpensive to operate, efficient, easy to install, provide the necessary radiation spectrum, but are very hot and difficult to dispose of.

- Metal halide lamps give light that is as close to natural as possible, but, unfortunately, they are not cheap, and are not particularly durable in operation.
- LED lamp differ in high service life, durability, simplicity in installation and an opportunity to choose radiation of a necessary range. Are expensive.
- Separate phyto lamps, they are LED and fluorescent. Manufacturers specially adapt them for use in greenhouses and conservatories. This is an expensive but most suitable lighting option.

No. 10. Excess Light Protection
Do not forget that in the summer there can be too much light, especially if the garden faces the south side, so it is necessary to provide options for protection from excessive solar radiation. These include the following activities:
- internal protection Are curtains and jalousie. It is better to use fabric, plastic and bamboo - aluminum can become too hot, and it will make noise when the fans are working. In a similar way, it will be possible to delay up to 40% of the sun's rays, but heating cannot be avoided;
- external protection allows to provide protection for 90%. Awnings and awnings for such protection are made of a special fabric that reflects light, so that neither excess light nor excess heat gets into the winter garden. For the hot southern regions, such protection is especially necessary if shade-loving tender plants are grown.

No. 11. Conservatory irrigation system
If you equip a very, very compact garden, then about a special irrigation system you don’t even have to think. It will be enough ordinary watering cans and good memory to add water in time.
For a more or less large-sized garden, manual watering will become hard labor, it will take too much time and effort, so you have to think about automation. Habitual for greenhouses, rain and aerosol types of irrigation are not appropriate here.
The best option for the winter garden is drip irrigation. From a source of water through a system of perforated hoses and tapes, water flows to the root system of plants. There will be no puddles. If you connect a system of sensors that measure the level of humidity, then water will be supplied only when it is really needed, and this guarantees optimal soil moisture.
Some types of plants draw some of the moisture from the air. For such greens, you must additionally humidify the air. You can use foggy installations, humidifiers or fountains, which will also perform a decorative function.
Do not forget that drainage is necessary to remove excess moisture.
No. 12. Selection of plants for the winter garden
When choosing plants for the winter garden in a private house, you must rely only on your own taste. But when combining different types, you already have to think about how to correctly combine them. The requirements for lighting, temperature and humidity are different for all varieties, and it is almost impossible to create several microzones with radically different conditions in one garden. Therefore, it is better to choose plants that require approximately the same conditions, and then combine them together.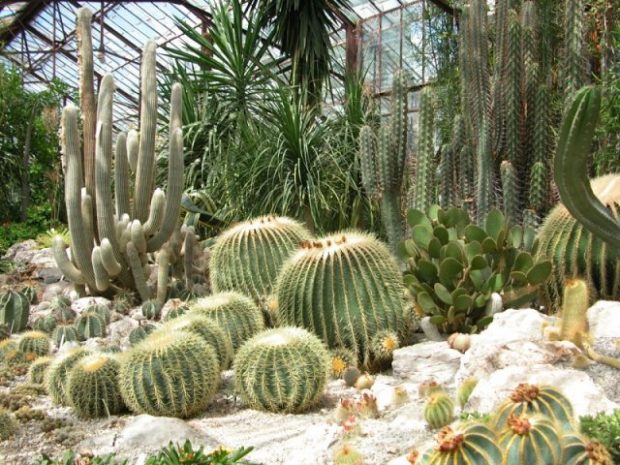
When choosing, consider the side of the world that the winter garden faces. If it is south, then heat-loving varieties are preferred.
Plants according to growing conditions can be divided into several types:
No. 13. Design and decoration of the winter garden
It is advisable to start work on creating a winter garden with designing. In special applications, a sketch is created on which the dimensions of the structure, windows, hatches and transoms are marked. Then the project is prepared, when it is created, lighting, ventilation, heating, watering systems, materials used, and the adjoining scheme to the house are thought out. The design phase involves the creation of drawings indicating all the details. Only with a serious thoughtful approach will it be possible to build a strong and reliable winter garden.
After the technical side of the issue has been thought out, you can move on to the pleasant and plan the internal arrangement of the winter garden in the house. Better foresee several functional areas:
- decorative zone - the base, plant compositions are grown here, fountains, sculptures, aquariums, etc. are installed;
- recreation area - A place to relax households.The space is equipped with comfortable chairs, hammocks, and if the area allows, you can put a dining table;
- communicative - These are paths and alleys that can be used to access plants and walks (if the garden has come out large);
- official - A place to store garden equipment, fertilizers and everything necessary for caring for plants.

Clearly follow any specific landscape style within a small conservatory is difficult, but common features can be used:
- for classic style symmetry is characteristic, elaborate figurines of animals and people, you can put a small fountain of the correct geometric shape;
- eco style - This is the maximum naturalness in the lines and choice of plants. Those species that grow in your area are perfect. In winter, they will delight you with a summer aroma. Try to do everything so that it seems that you just covered a piece of nature with a glass cap. No severity, symmetry and pretentiousness;
- high tech - this is the accuracy and conciseness of the lines, a combination of greenery with metal and concrete. Such a garden will complement the modern home or office;
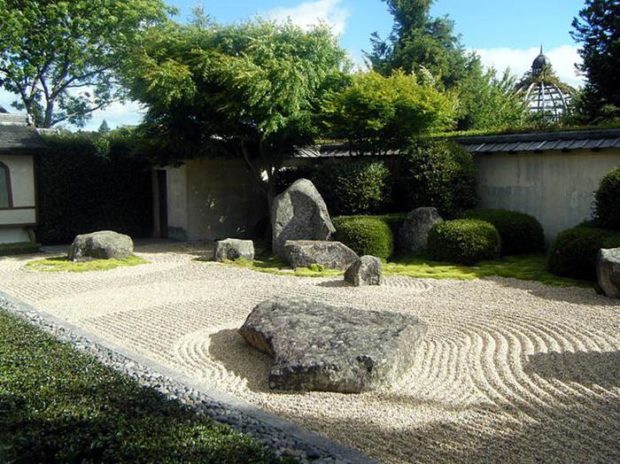
- Japanese style - These are low trees, stones, small pagodas, streams and asymmetry. To correctly recreate it, you will have to carefully study the philosophy of this style;
- country Close to eco-style. It involves the cultivation of not very exotic plants, focuses on local flowers and herbs. All this is decorated with natural materials: vine, stumps, clay pots.


No. 14. What else?
Do not forget to find out in advance what soil the selected plants will need, what fertilizers will need to be bought, how much money will be spent on providing all engineering systems. Also do not forget to consider the location of the outlets.
Choosing furniture for the recreation area, prefer products made from natural materials: wood, rattan, vine.
Examine whether selected plants can be adjacent to each other. Also decide in advance how you will plant all varieties.