10 tips for choosing a voltage regulator
How many equipment have killed voltage drops! If you do not want to be among the victims and suffer serious material damage, you should think about buying a voltage stabilizer in time. Yes, you will have to spend money, but imagine that during problems with electricity, a refrigerator, a TV, a washing machine and other expensive equipment will not be affected, as, for example, with not so far-sighted neighbors. The advantages are clear - all that remains is to figure out which voltage regulator to choose so that it best suits your needs.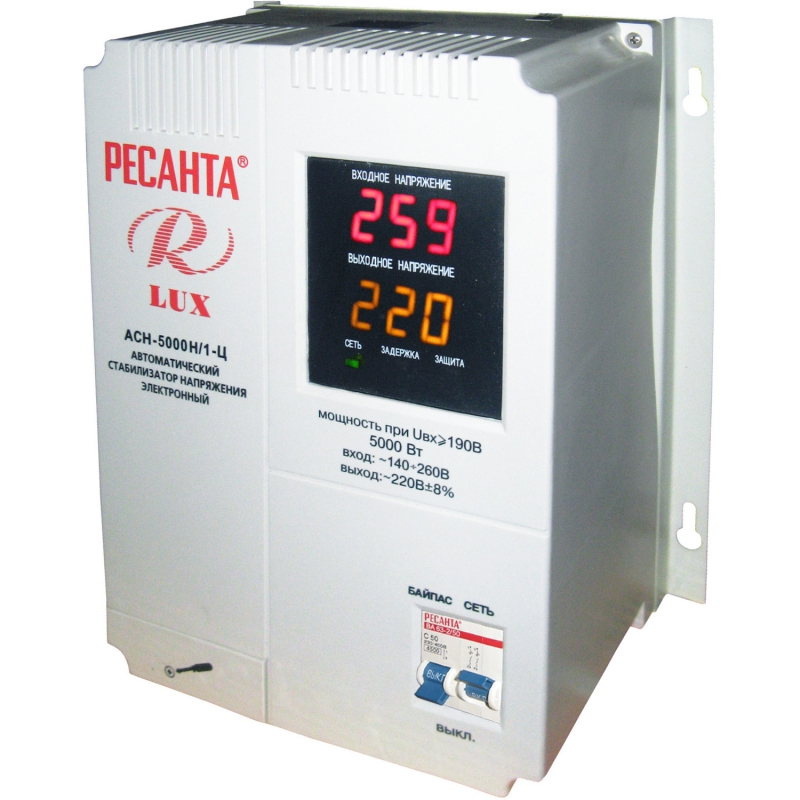
Do you need a voltage regulator?
Even a person far from electrical engineering can understand from the name of this device that its main task is to equalize the voltage that enters the home so that the equipment does not suffer from sudden changes in this voltage itself. The electricity supplier must provide a voltage of 220 V (± 10%) and a frequency of 50 GHz. And if the frequency is usually all right, then there are problems with voltage.
With a serious power surge, the devices simply fail, and with constant small fluctuations, the service life of the equipment is significantly reduced.
Who needs a voltage regulator?
- Residents of country houses, summer residentsas well as living in the countryside. Fluctuations in power networkslocated far from the city is not uncommon.
- Residents of urban apartmentsif there are problems with voltage stability. Serious changes can produce noise in the speakers and on the screens, blinking lights, changing the sound of the refrigerator and washing machine. Less significant differences can be detected with a multimeter. Measure voltage in outlet at the peak of electricity consumption (in the evening, for example) and with a minimum consumption (working day). The permissible deviation is 10%, i.e. for a 220 V network, the voltage can be 198-242 V. If the fluctuations are more significant, then it's time to think about buying a voltage stabilizer.
A voltage stabilizer is an adapter between a power source and all electrical appliances. It is able to increase / decrease voltage, or turn off the power in case of too low (less than 160 W) or high (more than 255 W) voltage. When choosing a voltage stabilizer, it is important to consider a lot of factors.
Network or trunk stabilizer?
Voltage stabilizers for the home are:
- networked. They plug into an outlet and are designed to work with one or more devices. These are often used when installing a computer;

- trunk. Used to connect all points of electricity consumption in the house, including lighting devices. Such a stabilizer is connected not to the outlet, but to the electric main.

Which voltage regulator is better to choose? Ideally, the trunk. But if you live in a city, then it will be appropriate to use only a network stabilizer with the most expensive and delicate equipment.
Types of voltage stabilizers
Relay stabilizer
Due to the low cost and high accuracy of regulation, such stabilizers have gained the greatest popularity. A power relay switches the transformer windings to get the desired voltage at the output. It is adjustable in increments of 5-20 V. The higher the number of relays, the higher the accuracy of the adjustment, but at the same time, the response frequency increases, hence frequent and small voltage drops, which can affect the operation of lighting devices (flicker).
pros:
- compact size, light weight;
- the ability to work in a wide range of temperatures (-30 ... + 400FROM);
- overload operation (several hours at a voltage of 110% of nominal and several seconds at 200% of nominal);
- high speed response;
- wide range of input voltage regulation, low sensitivity to distortion;
- longevity up to 10 years;
- low noise.
Minuses:
- step stabilization and, as a result, a change in the level of illumination;
- a large number of nodes in the design reduces reliability.
The equipment is optimally suited for networks with small and infrequent voltage drops.
Electromechanical stabilizer
The stabilizer operates by moving a contact transformer across the winding, which is driven by a servo drive. There are network and trunk.
pros:
- work with heavy loads;
- ability to withstand severe power surges (a few seconds at a voltage twice as high as the rated voltage);
- smooth voltage adjustment;
- noiselessness in the absence of sharp surges;
- input voltage can be almost anything;
- high accuracy of stabilization;
- low cost, but there are expensive models with high speed response.
Minuses:
- the response speed to a voltage surge is limited by the brush speed (10-15 V / s);
- the higher the power, the greater the weight of the device;
- equipment will not work at temperatures below -50C and more +400FROM;
- noise at the time of voltage stabilization;
- brushes and servo need regular replacement (every 3-7 years).
Such a stabilizer is well suited for networks with stably low or high voltage. The lights will not flicker.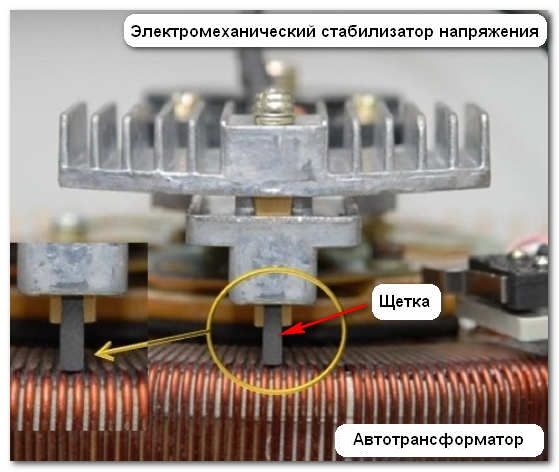
Thyristor and triac stabilizers
By the principle of operation, they remind relay stabilizers, but semiconductor switches, triacs or thyristors switch here between the windings. Due to this, the speed increases, the noise decreases, the work efficiency increases. Many models are equipped with a display, which displays the input and output voltage.
pros:
- reliability and durability;
- work with low and high incoming voltages;
- many models can withstand temperatures up to -200FROM;
- details hardly wear out, since there are no moving elements;
- performance;
- noiselessness.
Minuses:
- high price;
- complexity of repair work;
- low resistance to overloads;
- the higher the accuracy of adjustment, the higher the number of steps, and the lower the speed.
Typically, such stabilizers are used to protect individual equipment (computer, washing machine) with frequent, but insignificant voltage drops.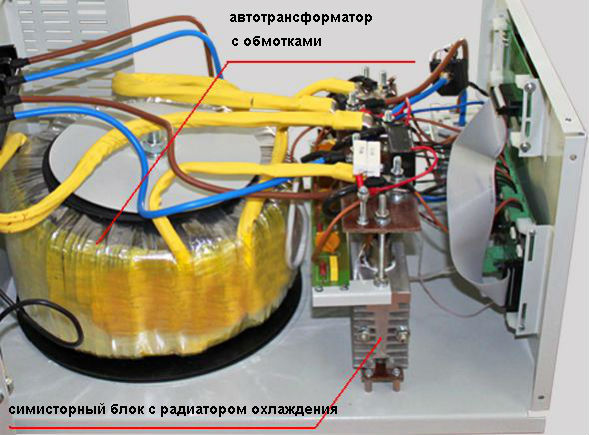
Inverter Stabilizer
The newest and most advanced stabilizers. They work on the principle of double energy conversion, due to which they lose the numerous disadvantages of another type of device.
pros:
- compactness;
- work with an input voltage of 115-300 V, while at the output we get a stable voltage of 220 V;
- high accuracy;
- minimum delay.
Minuses:
- price;
- the operation of the equipment requires constant cooling, for which the fans are responsible, so you have to put up with a little constant noise.
The equipment is suitable for any type of equipment.
Combined stabilizer
Combines the advantages of relay and electromechanical devices. If there is a sharp voltage surge, then the relay mechanism is turned on, since speed is important here.At voltages close to normative, the servomotor works.
Single phase or three phase?
For most apartments and houses, a single-phase stabilizer is suitable, since the network in them is single-phase. In the presence of a three-phase network, you can take a three-phase stabilizer, or you can take three single-phase ones.
Power
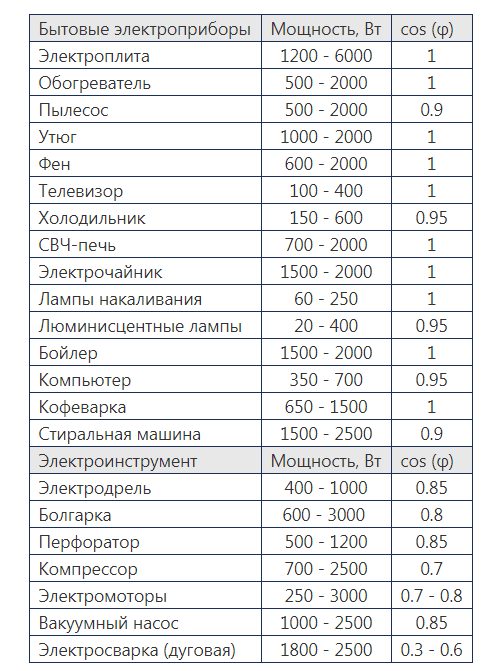
The power of the stabilizer must be selected with a margin of 20-30%. With network devices, everything is clear, but with the backbones you have to apply a simple calculation:
- it is necessary to calculate the total power of all devices and lighting objects, taking into account the active and reactive load;
- active load typical for appliances that convert electricity into heat or light (light bulb, heater, iron, etc.). Unit of measurement - kW;
- reactive load typical for appliances with electric motors and capacitor banks. Their full power consists of the active and reactive parts, measured in kVA. To calculate the power consumption, it is necessary to divide the active power by cos (φ), both parameters must be indicated on the device. If it is not specified, then take the average value - 0.7;

- total power calculated according to the formula below, where P is the active power and Q is the reactive;

- note that there are devices whose inrush current significantly exceeds the rated current.
Voltage stabilized range
This is one of the key characteristics of a voltage regulator. For example, a range of 130-270 V means that the device can provide a stable voltage of 220 V at the output with an input voltage of 130 to 270 V. At a higher or lower voltage, the stabilizer will first change the output voltage by 15-18%, and then turn off everything appliances.
To understand which voltage regulator to choose, you need to determine the extent to which the voltage in your house jumps. Measure for several days at peak times (morning and evening). Consider the lowest and highest value when purchasing.
Stabilization accuracy
This indicator indicates how much the output voltage will differ from the nominal (220 or 230 V). For most electrical appliances, stabilization accuracy of 5-7% will suffice. For lighting fixtures, an accuracy of 3% would be better, which would ensure no flicker. Ideally, take a main stabilizer with an accuracy of 3%, and network can have an accuracy of 5-7%.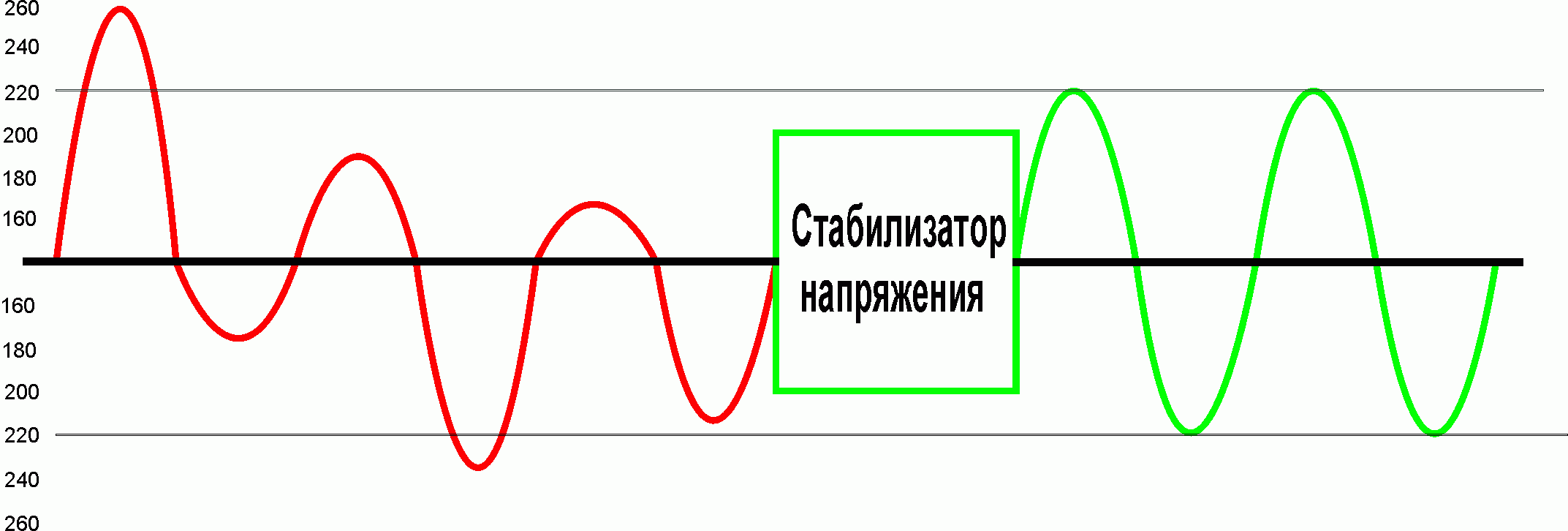
Installation method
Stabilizers are installed wall or outdoor. There is already someone more convenient. It is important that the room is dry, free of dust and critically low or high temperatures. There should be room around the appliance for efficient cooling. If we are talking about a private house, then it is optimal to install a stabilizer near switchboard, and basement or attic rooms are definitely not suitable.
What else?
Also, when choosing, pay attention to the following parameters:
- the presence of a display is optional, but it will be useful if it is important for you to monitor the input and output voltage;
- manufacturer name very important. The stabilizers Ortea (Italy) of the Gemini, Vega, Antares, Aqarius, Orion, etc. series showed themselves well. Among domestic manufacturers, we note Bastion, Resanta (assembly in China), and Calm.
Some household appliances do not need to be connected to the stabilizer. Many heaters equipped with heating elements can operate with significant voltage surges, and such devices as a pump and welders, have high starting currents, as a result of which the protection can trip in the stabilizer, and the entire network will turn off.