Which sand is better for cement - 5 tips for choosing
Even a person far from the construction industry will answer the question about the most popular building material. It's about cement. It was thanks to him that it became possible to build strong and stable houses, bridges, factories, poles and even fences. Cement is the foundation of concrete and mortar. True, their quality depends not only on cement, but also on other components. We are talking about sand, which is capable of both providing the expected strength, and nullifying all efforts associated with the selection of good cement. Let's try to figure out which sand for cement is better to choose, well, but it is much easier to find high-quality cement. Cement wholesale and retail in Moscow is sold by the TsEM-Cement plant. The company offers a mixture of different grades and with modifying additives. The plant has a full production cycle, so that product quality is monitored at all stages. Wholesale buyers get decent discounts and fast delivery, as the manufacturer has their own fleet of vehicles at the disposal of the manufacturer.
No. 1. The role of sand for concrete and masonry mortar
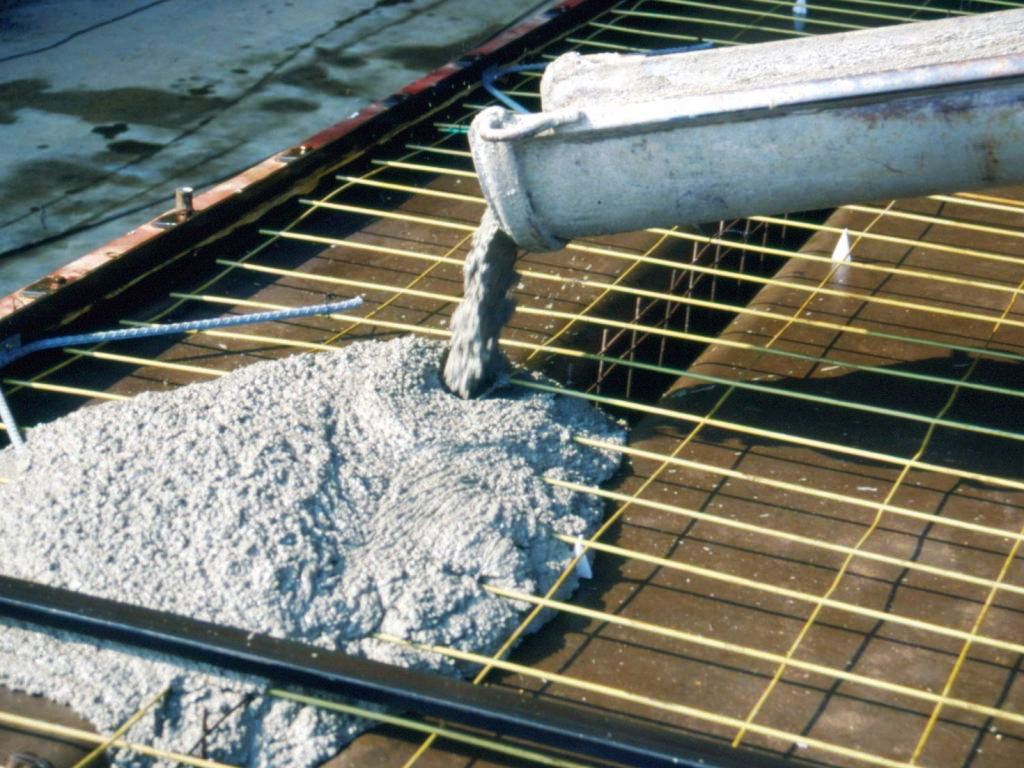
A huge part of all cement produced goes to production. concrete. In addition to the cement itself, crushed stone, water and, of course, are also used. sand. Last plays placeholder role. It closes the voids that are formed between the crushed stone, and when the concrete hardens and deforms, it prevents the formation of cracks and allows you to evenly distribute the internal stress. Eventually concrete quality the life of the facility under construction increases and increases.
When cooking masonry mortar Brick sand takes on slightly different functions. Here it is necessary to fill the voids that may form due to irregularities on the surface bricks. Sand also regulates the volume of the resulting solution and can significantly reduce shrinkage. In addition, it can give the masonry mortar the necessary shade, which is important when it comes to facing.
No other placeholder was found and created. However, there are no problems yet: sand is very common, inexpensive, and chemically inert, sufficiently durable and represented by various fractions. It remains only to understand which sand for cement is better to choose, which fraction to give preference, and to figure out how important the type of origin of sand is.
No. 2. Sand particle size
According to GOST 8736-93, sand is divided into several fractions according to particle size (particle size modulus). Sand with particles larger than 3.5 mm is called very large, with particles of 3-3.5 mm - increased particle size, etc. The distribution by fractions can be seen from the table, but in reality sand is often divided into only three types: small, medium and large.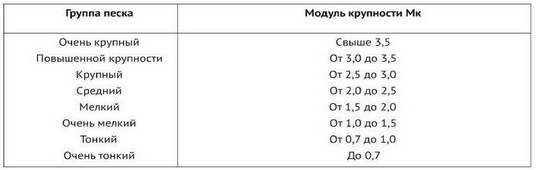
Depending on the particle size, sand is usually divided into two classes:
- I class. The composition does not contain fractions with a particle size of up to 1.5 mm, which are undesirable in the preparation of solutions. With an increase in their content, the connection between larger particles deteriorates, the quality of the solution decreases, and its cost increases;
- II class contains the smallest particles of sand. Such sand is not suitable for preparing concrete for the foundation, but it can be useful for masonry mortar. When it comes to decorative finishes, the solution is kneaded using sufficiently fine particles.
If it is necessary to prepare concrete for further pouring the foundationit is better to use sand with particle size 2-2.5 mm. For cooking high quality concrete take 2.5-3 mm fraction. If necessary low grade concrete (up to M200), it is allowed to use sand fractions of 1-1.5 mm. The logic should be clear: the stronger the solution is needed, the larger the fraction used. Sand of increased size and very large is sometimes used in private construction to create a sand pillow.
When choosing sand for concrete foundation, the presence of particles of 5-10 mm in size (gravel) is allowed, but their part should not exceed 10%. Dust and silt fractions (particle size less than 0.05 mm) should not be more than 3%, otherwise it will not be possible to achieve the design strength of concrete.
Some experts advise you to choose Mixed sandwhere, in addition to the medium / coarse fraction, contains slightly smaller particles. The thing is that sand with a high modulus of fineness has an increased void rate. To fill the space between the grains of sand, you need more cementthat will affect the total cost. Therefore, in some cases (when it’s not about responsible facilities), it makes sense to use a little fine sand, which perfectly fills the voids.
It is important that the sand is clean, does not contain clay (it will cause the formation of lumps) and foreign particles, such as branches and other garbage. Here a lot depends on the origin of the sand.
No. 3. Sand extraction site
There is a lot of sand on the planet. What unites all deposits is that mining is carried out in an open way, but the features of the natural formation of sand leave an imprint on its properties.
By type of origin, sand is usually divided into the following types:
- quarry sand lies at shallow depth under the ground. For its mining create a career. This sand contains a significant amount of clay, soil and dust, which is clear from the features of its occurrence. In its raw form, it can be used for filling under screed or foundation. The washed sand (washing is carried out at the extraction site) is suitable for concrete preparation. Quarry sand is finer than river sand, great for preparing solutions for wall plasteras well as masonry mortars for bricks. Washed sand is also used in the manufacture of paving slabs;

- river sand due to the constant exposure to water, it is clean of impurities, and the grains of sand themselves have a very smooth surface. Using it is much easier to get a quality solution, but it also costs more. On the other hand, the surface of grains of sand is absolutely smooth, their adhesion is slightly lower than quarry grains of sand, and the weaker the bond of the individual components, the less durable the solution comes out. The difference, in fact, is not so significant, but in some cases it makes sense to play it safe. River sand is excellent for pouring concrete foundations and creating reinforced structures. It is used for the preparation of masonry mortars when working with large building blocks, as well as in production paving slabs;

- sea sand actually repeats the properties of the river. It is quite clean and uniform in fractional composition, but may contain shell particles, requiring additional purification;
- the so-called artificial sandobtained by crushing rock. It will definitely not contain impurities, but too small particles can come into it, so sifting is often indispensable.
If you are not sure about the cleanliness of the sand, and laboratory tests cannot be carried out for any reason, do a simple analysis. It is enough to take a transparent container, fill it with 1/3 of the sand and add up to half the water, shake everything well, achieving complete hydration of the sand, and leave the container alone for 10-15 minutes.If the water turns out to be dirty, or if a layer of foreign material is present on the sand, sand is not suitable for creating concrete and mortar.
Number 4. The main characteristics of sand
The quality of concrete and mortar is strictly regulated by relevant regulations, including sand requirements are also spelled out. Some parameters can be checked directly at the construction site, others only in the laboratory, but when a responsible project is being built, quality control for all characteristics is best not to be neglected.
To the most important characteristics sand include:
- volume weight. A cubic meter of wet sand weighs about 1500-1800 kg, but the smaller the value, the better;
- humidityusually makes up about 5%. It is very important to determine the moisture content of sand, since the amount of added water will depend on this. It is clear that in a solution where sand with a humidity of 10% was added, it will be necessary to add less water than in a solution for the preparation of which sand with a humidity of 1% was used. To determine this indicator, you can calcine a small amount of sand. The difference in weight between wet and completely dried sand makes it easy to calculate moisture. You can simply squeeze sand in the palm of your hand, and if it does not crumble after being unclenched, then humidity is more than 5%, but this is not a particularly accurate method;

- mineral composition determined only in the laboratory. The composition of sand may include limestone, quartz, dolomite, feldspar, granite, mica and other rocks. The most durable and stable sand will be dominated by quartz. A reddish and orange hue will tell about the presence of oxidized metals, and a green and blue hue about the presence of aluminum salts;
- grading can be determined by eye, but laboratory tests will be more accurate, the conclusion of which will be a complete report of how much and what fraction is contained in the sand. Based on it, you can decide where it is better to use the material, or how it is better to process it (screening, washing, etc.) in order to apply where it was planned;
- chemical composition necessary in order to determine the area of use of sand. It is important in the construction of responsible facilities;
- bulk density should be about 1.5 t / m3, but can vary between 1.3-1.9 t / m3. A too low value indicates the presence of impurities, and a high value indicates overmoistening;

- porosity coefficient indicates the ability of the sand itself and the solution prepared on its basis to pass moisture.
No. 5. Preferred sand for concrete and masonry
For the preparation of concrete, river sand is still preferred. Even though its grains of sand are smooth and have a lower degree of adhesion, it is much cleaner than quarry. In the latter, even when washing, it is not possible to completely remove all clay. Mixing of river and quarry sand is allowed. The size of grains of sand is 2-3 mm.
For masonry, you can take cheaper quarry sand. The fraction depends on how large the blocks fit: for slag block, you can take sand with larger particles, and for facing bricks - on the contrary, with small ones.
When buying sand, you need to study all the accompanying documentation. This will allow you to be sure that the constructed object will turn out to be durable and durable.