8 tips on which pipes to choose for a gas pipeline: diameter, material
The organization of the gas pipeline is an important step towards ensuring the comfort of your own home, but at the same time, it is complex technical work associated with great danger. The design, selection and installation of pipes of a certain material and diameter is best left to professionals, but everyone needs to know the basic principles and nuances of arranging gas supply. We figure out which pipes for the gas pipeline are better to choose, which can be used everywhere, and which are suitable only for underground installation.
No. 1. Classification and diameter of gas pipelines
When choosing gas pipes, first of all, it is worth considering gas pressure. Depending on this indicator, gas pipelines divided into such types:
- I-A - network with a pressure of more than 1.2 MPa. For such sections, pipes with a diameter of 1000-1200 mm are chosen; they are usually used to connect steam plants, thermal stations and turbines;
- I - gas pipelines high pressure 0.6-1.2 MPa, such systems operate in places of gas distribution and transportation;
- II - gas pipelines high pressure, but its performance is slightly lower than in the previous case, 300-600 kPa. The diameter of the pipe is 500-1000 mm, they are used to supply gas from gas distribution facilities to homes, industrial, social and other facilities;
- III - gas pipelines medium pressure, 5-300 kPa, pipes with a diameter of 300-500 mm are used. Such networks are used for pumping gas from the main to an inlet gas pipeline near residential buildings;
- IV - gas pipelines low pressureup to 5 kPa. Pipe diameter up to 300 mm. Such pipes are used to transport gas from the inlet gas pipeline to houses and directly through the house to gas consumption points. It is with this type of pipe that consumers face when organizing gas pipeline within a private house or apartments.

No. 2. The method of laying gas pipes
Gas pressure is, of course, a fundamental factor of choice, but not the only one. It is also necessary to take into account the operating conditions of the gas pipeline, i.e. features of its laying.
According to the installation method, the gas pipeline is divided into such types:
- underground. It is considered the safest, especially when it comes to high pressure gas pipelines. However, with this method of laying it is necessary to reckon with such factors as the depth of freezing of the soil, its density and the likelihood of corrosion processes. To transport dried gas, the depth of the gas pipeline should be about 0.8 m. Installation of pipes for transporting wet gas is carried out below the level of freezing of the soil. Suitable for underground installation steel and polyethylene pipes. The latter are used more and more today
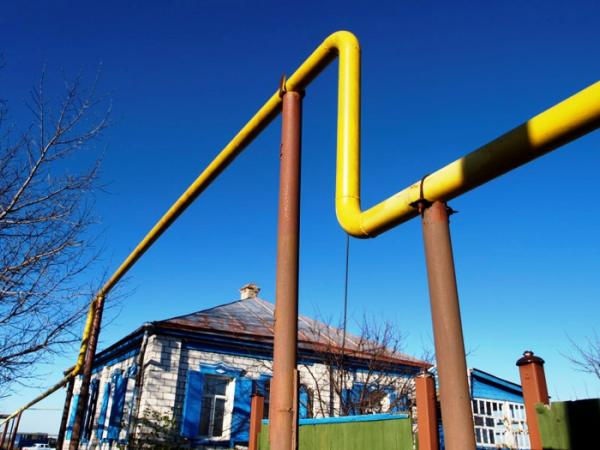
- aboveground. It is inferior in reliability to the underground one and is used only when it is impossible to hold pipes underground. These are rivers, canals, ravines and other areas difficult from the point of view of relief. Overhead installation is allowed to be performed on the territory of enterprises. Best suited for these purposes. steel pipes;

- internal gas pipeline in the house and apartment performed in an open way.In order not to draw attention to the pipes, it is allowed to install them in pre-prepared strobes, but it is only necessary to hide the gas pipeline behind easily removable panels - there must always be access to the pipes. The internal gas pipeline is organized by steel, rarely copper pipes.
No. 3. Gas pipe material
More recently, there was no particular choice, and on all sections of the gas pipeline, from large nodes to consumption points in houses, exclusively steel pipes were used. Today an alternative has appeared in the form of low-pressure polyethylene pipes. Copper pipes are also used. It is unlikely that they will have to suffer the torment of choice, since each of these materials has strictly defined operating conditions:
- steel pipes can be with different wall thicknesses. Thick-walled products are used for arrangement high pressure gas pipelines. If we are talking about overhead installation, then there is no alternative to steel pipes. These are strong, durable and reliable pipes that can cope with a serious load. Thin-walled pipes are suitable for organizing a low pressure gas pipeline, incl. to equip the system gas supply inside the house;
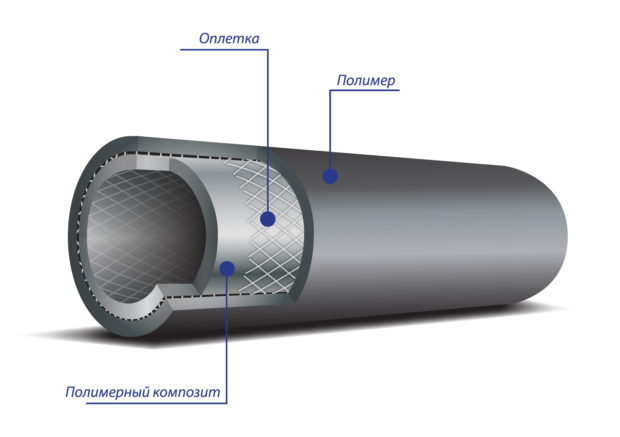
- polyethylene pipes used for underground installation gas pipeline with different pressures. There are products that withstand operation at a pressure of 1.2 MPa. They beat the steel counterpart in weight, price and ease of installation. Not suitable for above-ground and in-house installation;
- copper pipes in many respects superior to steel, but their mass use is impossible because of the high price. Overhead installation using such pipes is not carried out, but it A great option for organizing a gas pipeline inside the apartment.
The network has information about the use as pipes for a gas pipeline metal-plastic and even polypropylene products, but these are still far from the most suitable options.
Number 4. Steel gas pipes
Steel pipes were previously the only way to organize gas supply. Today, when there are alternative solutions, steel still remains in the lead, winning in terms of versatility and breadth of scope. For gas pipelines, steel structures are made in different ways. Seamless cold and hot rolling tubes, as well as welded tubes with a spiral seam, are suitable. The use of a particular type of pipe depends on the pressure in the gas pipeline, the temperature regime and the characteristics of the transported gas.
In any case, to create gas pipes high quality steel low in carbon (up to 0.25%), sulfur (not more than 0.056%) and phosphorus (up to 0.046%). Even better if the steel passes anticorrosive processing, which can significantly increase the life of the pipeline.
TO main advantages of a steel gas pipeline relate:
- high strength, but in order for the design to be leakproof, welds should be performed as efficiently as possible;
- universality. Steel pipes can be laid above ground and underground, inside and outside the premises;
- functioning over a wide temperature range;
- ability to withstand high pressure;
- relatively long service life. Subject to all installation and operation rules, it is possible to count on a period of uninterrupted operation of about 40 years.
Among the disadvantages it is worth noting:
- complexity of installation work;
- high price;
- poor flexibility;
- susceptibility to corrosion and condensation;
- a lot of weight.
The versatility of steel pipes is achieved by a wide variety of products: products with different wall thicknesses and diameters can be found on the market. Pipes may differ in other properties, and all the basic information about the product can tell the marking.
The main parameter of the steel pipe is conditional diameter, marked as remote control. This is, in fact, the inner diameter of the pipe, which determines its throughput.It can range from 6 to 150 mm. For an internal gas pipeline, for example, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm are selected; for gas distribution systems, pipes of at least 50 mm in diameter are necessary.
Outside diameter depends on wall thickness. The latter parameter ranges from 1.8 to 5.5 mm and sometimes more. For overhead laying use pipes with a wall thickness of at least 2 mm, for underground - at least 3 mm. In some cases (under difficult operating conditions), reinforced pipes with a wall thickness of 5.5 mm or more may be required.
Keep in mind that thin walled pipes only used in low pressure systems. Such products are lightweight, flexible enough, so with their help you can mount a network of complex configuration. The connection occurs by soldering or by creating threaded connections. On the other hand, such pipes have high thermal conductivity: condensate can accumulate on them, which negatively affects the material itself, leading to its corrosion. That is why gas pipes are protected by several layers of oil paint.
In areas with high pressure use thick-walled pipes. These are robust constructions, but the functionality of the entire system will largely depend on the quality of the connection of individual sections. After welding monitoring is required.
On pipes with a DN more than 159 mm and a wall thickness of more than 3.5 mm, marking is applied directly to the product. In other cases, all information about the pipes is on the label, which must be present on the package. If the letter H is indicated in the marking, then we are talking about pipes with knurled threads, the letter P is a threaded thread, D is an elongated thread, M is the presence of a coupling.
The quality certificates for steel must contain information about the manufacturer, grade, category and group of steel, melting and batch numbers, confirmation of compliance with GOST. The manufacturer must carry out tests and check whether the product copes with standard pressure. There should be no defects on the pipe.
If you delve into the theory, it’s worth highlighting a very important point - depending on production conditions, steel can be:
- boiling. In the manufacturing process, it is not completely deoxidized, therefore, contains an increased amount of unnecessary impurities. This is a more brittle and corrosion-prone steel, not very good in weldability. It can be used for an internal gas pipeline and in seismically stable conditions;
- calm steel has a more uniform structure and is characterized by a minimum content of impurities. It is a durable material that welds well and withstands decent loads. Such pipes may be used even where there are vibration loads;
- semi-quiet steel - in terms of composition and performance, a cross between boiling and calm. It is strong enough and is often used instead of calm.

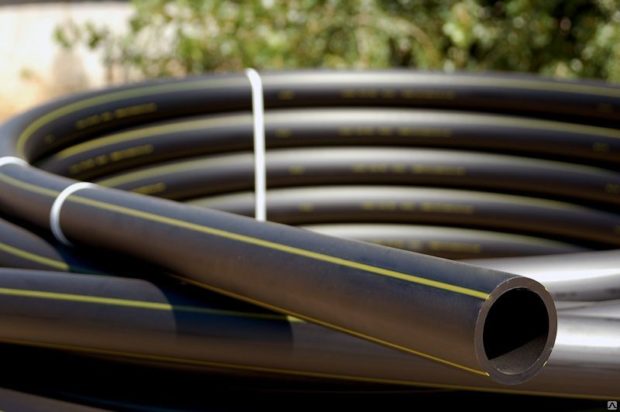
No. 5. Pipes for a gas pipeline made of low pressure polyethylene (HDPE)
Pipes from HDPE have recently been in no less demand than steel pipes. It should be noted right away that the phrase “low pressure”, which appears in the name of the material, refers to the peculiarities of pipe production, and not to the operating conditions of the gas pipeline. There are polyethylene pipes that withstand pressure up to 1.2 MPa. What makes us abandon the proven option with steel pipes and use polymer ones? The answer to this question lies in the advantages of the material.
The main advantages of polyethylene gas pipes:
- light weight;
- quicker and easier installation without the use of complex expensive equipment requiring special skills;
- strength, ductility and flexibility make it easy enough to circumvent possible obstacles in the pipeline. The maximum allowable bending radius is 25 pipe radii.Flexibility allows the pipeline to remain integral with small movements of the soil;
- the ability to withstand pressure up to 1.2 MPa, so that such pipes can be used on almost all sections of the pipeline;
- corrosion resistance, ability to withstand the effects of aggressive substances;
- high throughput, as the inner surface of the pipe is smooth. With the same diameter as a steel pipe, polyethylene will have a throughput of about 30% higher;
- pipes from HDPE are produced in large lengths, which allows for fewer connections, due to which integrity and reliability of the structure are achieved;
- polymeric materials do not conduct stray current;
- low cost when compared with steel or copper counterparts;
- durability of at least 50 years, and subject to all conditions up to 80-90 years.

Cons also have:
- polyethylene pipes must not be used in areas where the temperature drops below -450C. Such a gas pipeline shall be located at a depth of not less than 1 m, at -40 at winter temperatures0With depth increases to 1.4 m, and in some cases laying pipes from HDPE is completely impossible. At low temperatures, performance may deteriorate, and durability may decline;
- pipes are also not suitable for seismically active areas;
- the pressure of more than 1.2 MPa of the HDPE pipe will not stand - only thick-walled steel will help here;
- sensitivity to ultraviolet rays does not allow for overhead installation - polyethylene pipes are suitable only for installation underground;
- due to the increased flammability of polyethylene, such pipes are not recommended for use indoors. Already at +800C material has the ability to deform and collapse;
- HDPE pipes are not suitable for laying gas pipelines in manifolds and tunnels. In such places, a steel counterpart is used;
- when crossing the gas pipeline with roads and other utilities, pipes must be hidden in a metal case.

It is better not to use polyethylene pipes for the installation of the gas pipeline indoors, but they are used more and more often for underground installation.
For the production of pipes used special pipe grades of polyethylene:
- PE 80 - black pipes with yellow inserts, withstand pressure up to 0.3-0.6 MPa;
- PE 100 - pipes with a blue strip, withstand pressure up to 1.2 MPa. When installing them, more serious efforts are made, since the material has to be heated to higher temperatures, but the quality of the connection in this case is at a height.
The diameter of HDPE pipes can range from 20 to 630 mm or more, even pipes with a diameter of 1200 mm are used. When choosing, it is also worth taking into account such an indicator as SDR Is the ratio of diameter to wall thickness. The smaller this value, the thicker the walls and the more durable the product in front of us. SDR ranges from 9 to 26.
The connection of polyethylene pipes is performed in one of the following ways:
- butt welding. The edges of the individual elements are heated with a special soldering iron until a viscous consistency is achieved, which allows you to safely connect two pipes into one;
- electrofusion welding involves the installation of the edges of the pipe in a special coupling, to which voltage is supplied, due to which heating and connection of the two segments occurs. Such a connection is more durable than the pipe itself and can withstand a pressure of 16 MPa.
When individually connected to the network, butt welding will suffice, and if, for example, gasification of an entire area takes place, it is better to use electrofusion welding - it is more reliable and tight.
To connect a section of a steel and polyethylene gas pipeline, special elements are used, one side of which is welded to steel, and the other to polyethylene.
No. 6. Copper pipes for the gas pipeline
Copper pipes are used in the organization of the gas pipeline system relatively recently.They can be used only for laying pipes inside the house at a pressure of up to 0.005 MPa. For this purpose, drawn or cold-rolled pipes with a wall thickness of at least 1 mm are used.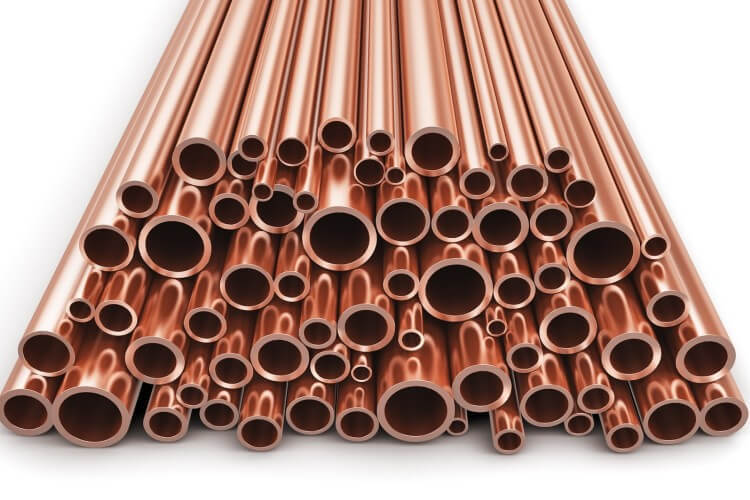
Benefits:
- attractive appearance. Gas pipes must not be hidden in walls or ducts - they should be easily accessible. Steel pipes can hardly be called an interior decoration, unlike the copper counterpart. It is unnecessary to hide such pipes - they look neat and attractive, fit perfectly into many interior styles;
- relatively simple installation, which is carried out using press fittings or soldering. In addition, copper pipes are easily cut;
- plasticity and the ability to create a network of complex configuration;
- sufficient mechanical resistance;
- resistance to aggressive substances;
- longevity up to 100 years.
Among cons high price, a small assortment on the market and high thermal conductivity, which can lead to condensation. The copper pipes are inferior in strength to steel pipes, but if we are talking about intra-apartment wiring, then this will not cause any special problems.
Number 7. Metal-plastic pipes for the gas pipeline
This is not the most popular option, but nonetheless encountered. These pipes can be created only the gas pipeline inside the apartment, connect gas consumption devices. SNiP 42-01-2002 allows the use of such pipes in buildings with a height of not more than 3 floors. Using fittings, you can make a connection with steel and polyethylene pipes.
Plastic pipe - This is a multi-layer construction. The outer and inner layer is plastic, between them is a thin layer of aluminum. Thanks to this design, numerous advantages:
- simple installation, so you can cope even without the help of a professional and a special tool;
- flexibility, you can get by with a minimum number of fittings;
- good tightness;
- low price.
Among cons limited scope. Plastic pipes are suitable only for laying inside buildings, they are afraid of prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays, and when heated above +400With the loss of tightness of the pipeline, as when cooling to a temperature of -150FROM.
Number 8. Safety requirements for laying a gas pipeline
The laying and operation of a gas pipeline carries great risks. To ensure complete safety, a number of rules must be followed. Before starting work on connecting a private house to a centralized gas pipeline, it is necessary to notify the local gas service about this. He must report on the pressure parameters in the gas pipeline to which the connection is made, and carry out technical coordination, after which a project of work is drawn up.
The relevant SNiPs and fire safety rules indicate how and where the gas pipes should pass in order to ensure maximum safety of their operation.
Overhead gas pipeline It is used in enterprises, as well as in cases where the soil has increased corrosion activity. In this case, they are guided by norms:
- the height of the pipe in the place of crowding should be at least 2.2 m, above the roadway - more than 5 m;
- in places where there is no movement of people and vehicles, installation at a height of 0.35 m is allowed;
- in places of intersection with power supply systems it is necessary to organize electrical protection.

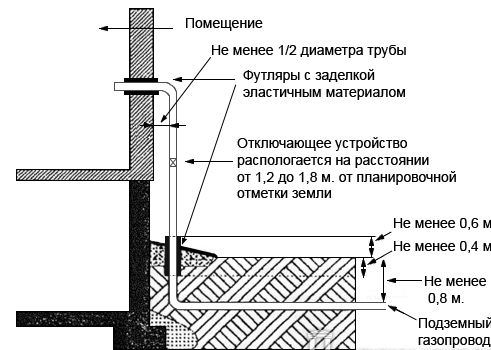
When underground laying gas pipes to the house you must adhere to the following rules:
- the depth of the pipes depends on the depth of freezing of the soil, but, in any case, not lower than 0.8 m. In areas where arable work or abundant irrigation is carried out, it is better to lay pipes at a depth of not less than 1.2 m;
- the distance of the gas pipeline from the road - at least 3 m;
- the distance of the low-pressure pipeline to the wall of the house is not less than 10 cm; entry into the dwelling is carried out by means of a sleeve.

Now the fun part is norms installation of gas pipes inside apartments and houses:
- gas pipes cannot be located in residential premises;
- installation of gas pipes in hard-to-reach places is prohibited; they cannot be hidden behind decorative cladding. The exceptions are those cases when the external decor can be easily removed if necessary to provide access to the entire pipe;
- the height of the gas pipe from the floor is at least 200 cm;
- installation of gas pipes is possible in rooms with a ceiling height of at least 220 cm and normal ventilation;
- when the gas pipeline is in the kitchen ventilation this room cannot be adjacent to the living rooms;
- gas pipe should not block window and doorways;
- the length of the flexible section of the gas pipeline should not be more than 300 cm;
- the ceiling above the gas pipeline must be trimmed with non-combustible stucco;
- for mounting gas column a steel or galvanized exhaust pipe is required, but in no case corrugated aluminum. Naturally, it is necessary to provide for the presence of a fuse in the column design, which will block the gas supply if the flame goes out;
- distance from thin-walled metal pipe to electric cable must be at least 25 cm to the visor - 50 cm;
- it is better to exclude the proximity of gas pipes and cooling devices;
- laying gas pipes in the kitchen on the floor, under the sink or near the dishwasher is prohibited;
- the pipe must be securely fixed to the wall using clamps and brackets.

As for pipe diameter, then in the calculation it is necessary to use such parameters as the length of the pipeline, gas temperature, allowable pressure drop, thermal power of the equipment and gas flow. To correctly calculate the diameter of the gas pipes, you need to use complex formulas - it is better to entrust this task to the designers. The network has online calculators that can quickly calculate the required diameter depending on the entered data. Special tables can also come to the rescue.