11 tips on which pipes for heating is better to choose: material, diameter
What should be the ideal home? The answer to this almost philosophical question can be sought for a long time, to list a lot of criteria and at the same time forget about the main thing. The key to comfort in the house is a comfortable temperature, and in a harsh domestic climate, it is possible to maintain heat only with the help of heating systems. Blood vessels, which many undeservedly do not pay attention to, are tubes. The stability of the functioning of the heating system depends on the quality of their performance, the right material and diameter. We figure out which pipes for heating are better to choose and get acquainted with the main characteristics of the most popular materials.
No. 1. What should be the heating pipes?
The purpose of the heating pipes is clear even to a child. They must transport hot water from boilerwhatever he is to radiators. This is a very important part of the heating system, on the quality of performance of which depends not only our comfort, but also safety.
The minimum set of requirements is put forward for heating pipes:
- strength and durability. Pipes must maintain integrity throughout their service life. If minor damage occurs and oxygen penetrates through them, the pipes may begin to rust from the inside and become clogged. Large damage will lead to leakage of the coolant, and this, in most cases, hot water. The consequences of all this can be disastrous;
- low noise in work, because constantly listening to the sounds of water boiling is a test for the nervous system;
- aesthetics. It’s not always possible to hide pipes in the walls or disguise themtherefore they should not frighten with the look and especially to spoil an interior.

No. 2. What to consider when choosing heating pipes?
There are no universal pipes that would function equally well in different rooms. To pick up best pipes for heating, i.e. the most optimal and suitable in specific conditions, it is necessary take into account such factors:
- temperature and system pressure, which largely depend on what kind of heating is used, individual or centralized. In individual systems, pressure rarely exceeds 2-3 atmospheres, and in centralized systems it can rise up to 16 atmospheres;
- type of pipe layingoutdoor or hidden;
- total area of heated housing;
- boiler design capacity and type of fuel (for private houses);
- operating conditions of the pipeline. This refers to the presence in some areas of unheated premises;
- the possibility of repairs.
All pipe specifications depend on the material of their manufacture - This is the most important parameter that must be considered when choosing.
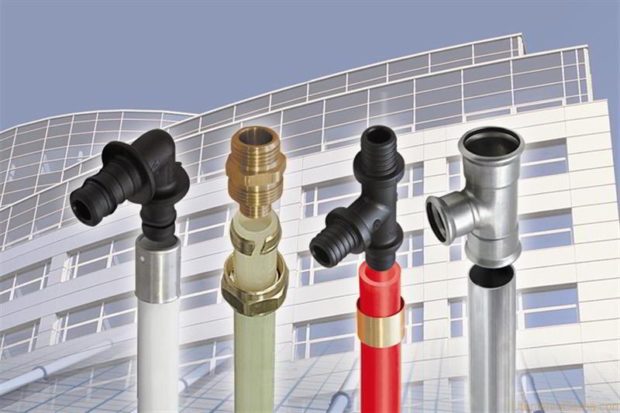
No. 3. Material of heating pipes: main types
In residential premises, these types of heating pipes are used:
- steel;
- from stainless steel;
- copper;
- polyethylene;
- polypropylene;
- metal-plastic.
Some of them (steel) are already outliving their own, others (polypropylene) are only conquering the market, but today all of the listed types of pipes are produced and used, because heating systems are very different and require an individual approach to installation.

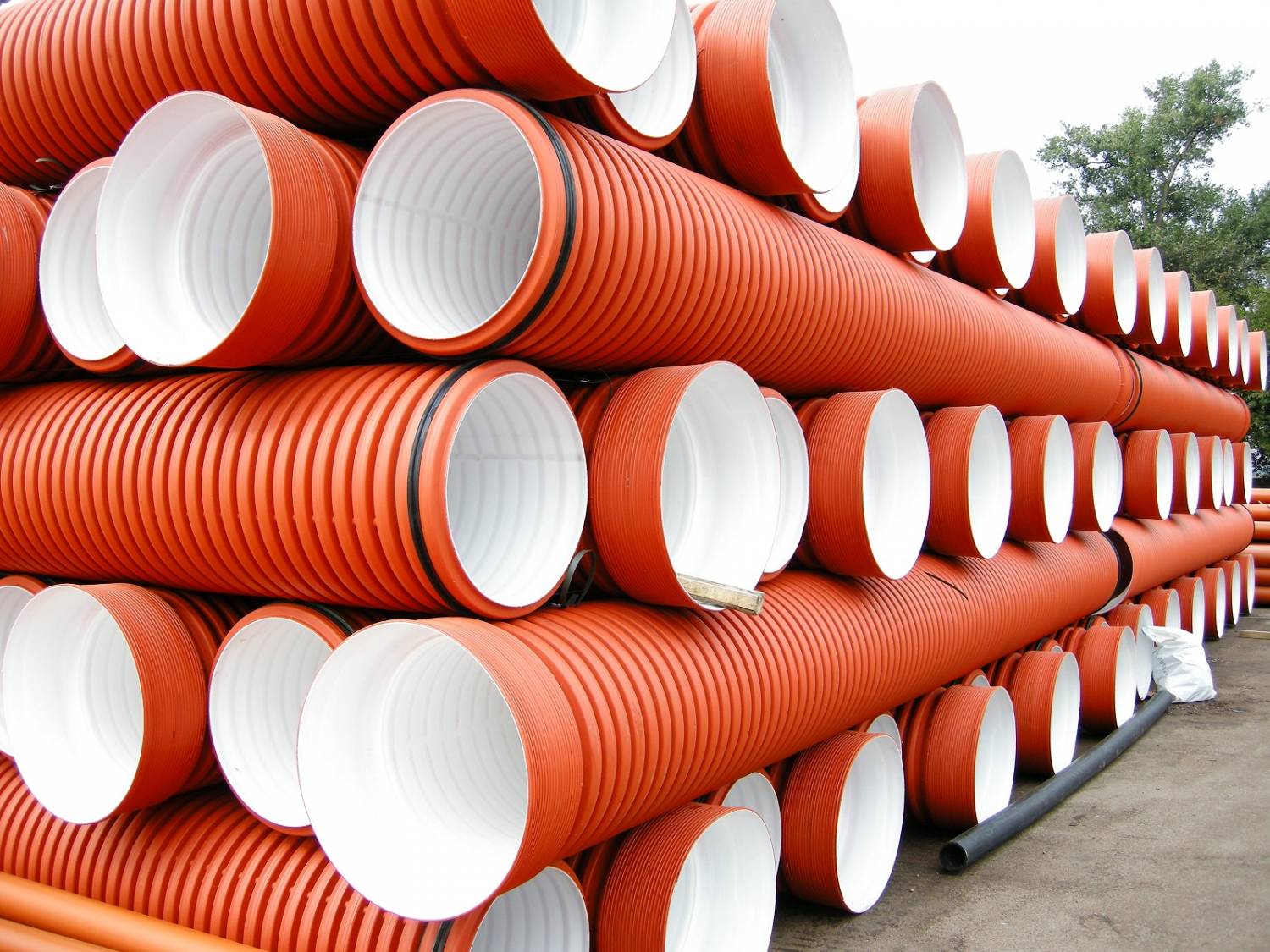
Number 4. Steel pipes for heating
Steel pipes for some time were the most popular and almost the only option for organizing a heating system. As time went on, worthy alternatives appeared, but steel pipes are still installed, however, mainly in private homes. They are made from quality carbon steel.
Main advantages:
- strength, reliability, high resistance to water hammer, pressure and temperature surges in the system. The material is not afraid of mechanical damage;
- low coefficient of thermal expansion, so you can do without compensators;
- high thermal conductivity;
- affordable cost is still one of the main reasons for choosing this type of pipe.

Minuses:
- low corrosion resistance. Gradually the pipes begin to overgrow, their throughput decreases. Moreover, corrosion processes can lead to leakage and pipe failure. To avoid this, it is recommended to protect the surface of the pipe by galvanizing;
- big weight and dimension;
- complicated installation. Individual elements are connected to the system using welding. If there are no skills with welding machine, then for the installation work you will need the help of professionals. Welding is also a high probability of damage to objects and surfaces in the vicinity. Alternative option - threaded connection individual elements, but threading is no less painstaking and time-consuming task. In addition, you will have to deal with numerous couplings, angles and tees, the main thing depends on the quality of installation - the integrity of the entire system;
- the material conducts stray currents that damage the inner surface of the pipes.

No. 5. Corrosion-proof pipes for heating
Corrugated stainless steel pipes are free from many of the disadvantages of the steel counterpart. They are used for arranging heating systems in new homes, as well as for reconstructing the heating system in old ones; they have gained great popularity in arranging warm floors, hot and cold water supply. Such a wide scope of application is explained by the main feature of this type of pipe - the ability to bend.
Benefits:
- stainless corrugated pipes are resistant to corrosion, do not collect scale on the walls, are durable;
- resistance to water hammer and external mechanical stress;
- slight thermal expansion;
- flexibility, and bends such a pipe with virtually no reduction in internal diameter. This is convenient when the space for installation of the heating system is limited. In addition, complex systems can be installed with a minimum of connections. This feature has made stainless pipes very popular when installing water heated floors;
- high heat dissipation;
- relatively simple installation;
- wide scope of use.
Minus, as you might guess, only one is the cost, but it pays off with the durability and ease of installation. Another unpleasant feature is the low durability of the sealing rings, about 30 years.
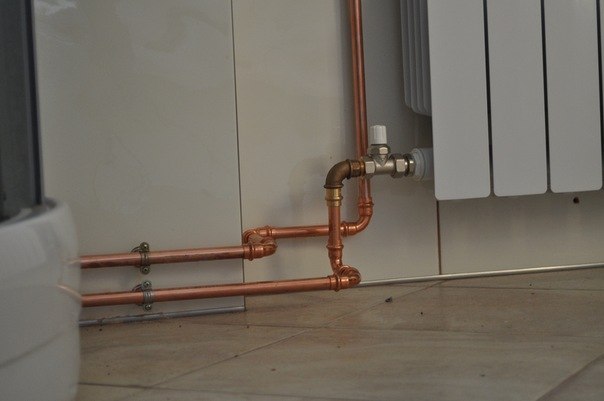
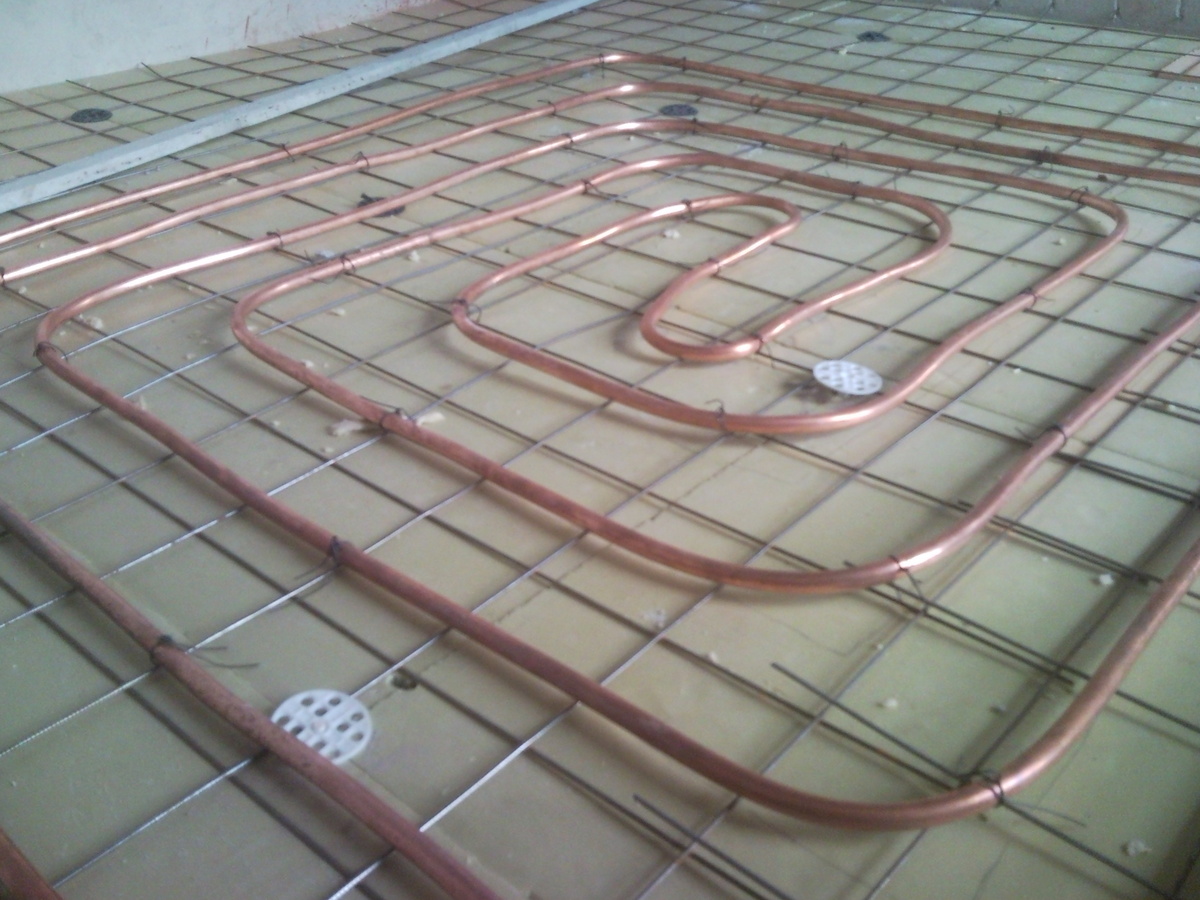
No. 6. Copper pipes for heating
We continue the study of metal heating pipes. Copper pipes began to be used as early as the XVII century and are still widely used, despite the advent of cheaper options.
Benefits:
- durability, comparing with the service life of buildings. Copper pipes and fittings do not lose their qualities for 100 years or more;
- corrosion resistance, high tightness, lack of ability to pass air and accumulate deposits on the inner surface, so over the years pipe throughput does not decrease;
- high thermal conductivity;
- resistance to temperature extremes (operating temperature range from -200 to +5000C) and pressure surges in the system;
- aesthetic appearance.

The main disadvantage is the high price. Not only is the material itself expensive, but also the main producers are concentrated outside the country. If we take into account the durability of the material and the absence of problems in the next 100 years, then the cost does not look such a significant drawback. If the question of choosing heating pipes does not rest on the budget, then copper pipes will be the best option. The installation process is specific, so it is better to seek help from professionals.
For a heating system to last for many years, it’s better do not combine copper pipes with unalloyed steel pipes. The latter will rust very quickly. If such a combination cannot be avoided, then let the steel pipes be in front of the copper pipes in the direction of water movement.
Number 7. Polypropylene pipes for heating
Polypropylene pipes made on the basis of polymers, there are several types of such pipes, but PPs pipes made of special propylene are usually used in a heating system. The materials of the thermoplastics group, which include all types of polypropylene pipes, are unstable to high temperatures, so for heating systems it is necessary take only reinforced pipes, preferably with fiberglass. So, for example, pipes of type PN25 are reinforced, withstand pressure in the system up to 25 atm and a temperature of +950C with short-term increase to +1200FROM.
Benefits:
- relatively long service life. According to manufacturers, durability reaches 50 years;
- corrosion resistance. The inner surface of the pipes remains smooth throughout its life, without compromising throughput. Due to the tightness, oxygen does not pass into the system and does not damage its metal elements;
- high mechanical strength;
- light weight;
- resistance to low temperatures. If water is frozen in the pipe, you can not worry about integrity - thanks to the ability to expand, the material will not be damaged and after thawing will take its original shape;
- tight connection, which is provided by special fittings and welding;
- relatively simple installation process. To connect the individual elements with fittings, they use a special welding machine, which is popularly called an iron and a soldering iron. It takes a few seconds to weld a joint, and learning how to use the machine is easy;
- low noise when moving water through pipes, especially when compared with metal counterparts;
- complete harmlessness to health;
- relatively low price. Polypropylene pipes will cost less than metal-plastic or stainless.
Among the disadvantages:
- inability to use in fire hazardous areas;
- high linear expansion results in the use of expansion joints.
Often low heat resistance, low rigidity and instability to water hammer are considered as disadvantages. This is due to the wrong choice of polypropylene pipes. For heating systems only reinforced products are needed that do not sag, withstand high temperature and pressure. In addition, the production process is of great importance: if the technology is violated, pipes of inadequate quality come out, so it is better to give preference to trusted eminent manufacturers.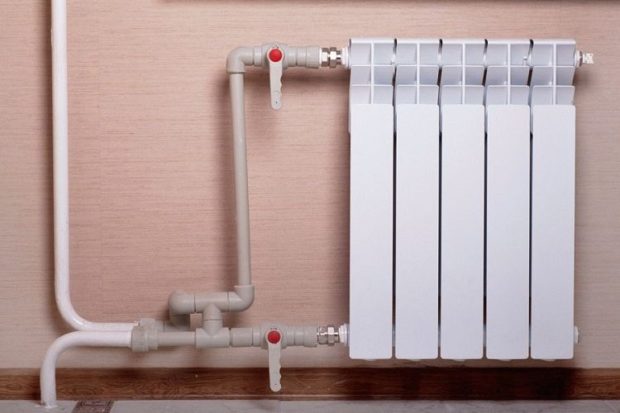
Number 8. PEX pipes, or cross-linked polyethylene pipes
Due to the special production technology, new molecular bonds appear in the structure of polyethylene, which provide additional strength and other useful properties. Today such pipes used not only in heating systems, but also during installation warm floors, as well as the arrangement of the hot water system.
Benefits:
- resistance to corrosion;
- durability along with sufficient flexibility;
- durability up to 50 years;
- the ability to withstand the temperature of the coolant up to 1200C, temperature and pressure drops;
- low weight.
Of cons we will highlight the high price for the pipes and fittings themselves and the need for special equipment for installation, so they are rarely used.
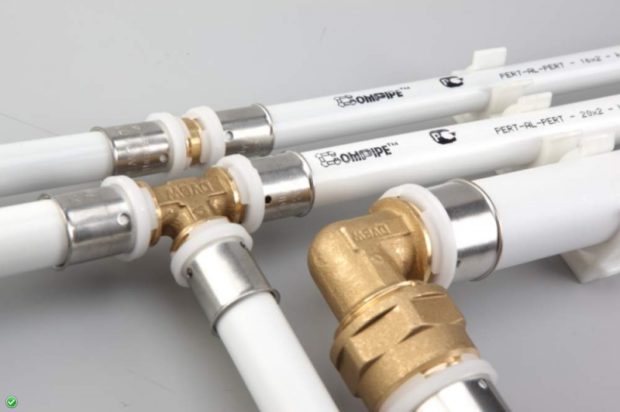
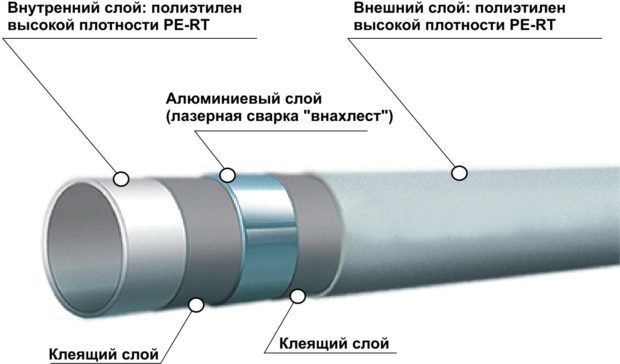
No. 9. Metal-plastic pipes for heating
Plastic pipes many call most balanced in terms of price / quality ratio. Such folk love has good reason. The product is made on the basis of polyethylene and aluminum foil: the outer and inner layer is plastic, in the middle there is foil, which plays the role of a frame and gives the structure rigidity, and binds all layers of adhesive with high adhesion to metal and plastic. A similar structure allows us to talk about mass the benefits:
- corrosion resistance, because the coolant is in contact only with plastic;
- the inner layer is smooth and does not accumulate deposits;
- tightness and impermeability of oxygen, so the metal parts of the system will be safe;
- the material bends well, so you can easily create an effective heating system even in rooms of complex configuration. Moreover, pipes are sold in bays of 50-500 m, therefore, in one section you can build a heating system in large spaces, and the fewer connection points, the less chance of leakage;
- durability up to 50 years;
- relatively simple installation;
- material does not transmit stray current.

Minuses:
- instability to mechanical stress and open fire;
- low resistance to ultraviolet rays, so it is better to use protection in the form of corrugated pipes;
- the price is two times higher than for polypropylene pipes.
It is also worth noting such a property as lack of linear expansion. On the one hand, you can safely wall the pipes into the walls without fear of damaging the future finish. On the other hand, if the coolant freezes, the material will not withstand the load and will tear. This is a good option for constantly heated visits.
The elements can be connected using a detachable, conditionally detachable or one-piece fitting. For the latter, special expensive equipment is needed, and when installing a threaded fitting, great care is required, since the nut can damage the pipe.
No. 10. So how best to choose heating pipes?
If expected independent installation of the entire heating systemit’s better to take polypropylene pipes. They are cheap, all joints come out completely tight, and even those with minimal construction experience will quickly learn how to work with a special welding machine for polypropylene. More time will be spent not on installation, but on calculation and preparatory work. The main thing is to purchase polypropylene pipes reinforced with fiberglass and stainless steel taps, and the whole system will work long and reliably.
Plastic pipes - also a good option. Although they are more expensive, no specific tools will be required for installation - only a wrench, but the connection risks losing tightness over time.
If you have the means, pipes from of stainless steel. Copper pipes will cost even more, but they are worth it.
No. 11. Diameter of heating pipes
Pipes made of different materials are presented in different diameters. In order to choose the most suitable value, it is necessary to study the entire scheme of the heating system and ask the help of specialists. The approximate diameter can be calculated independently. Parameters such as floor areaon which thermal power depends, and coolant speed.
Many mistakenly think that the larger the diameter of the pipe, the higher the efficiency of the system. In fact, when choosing too large pipes, the pressure in the system decreases, and the heating disappears altogether - warm water cannot go around the entire pipeline system and radiators. The smaller the diameter, the higher water flow rate. Ideally, the speed should be higher than 0.2 m / s, but less than 1.5 m / s, otherwise the process of circulation of the coolant will be too noisy.
The diameter is selected based on the calculation of the required heat output. For rooms with a ceiling height of up to 3 m per 1 m2 100 watts of energy are needed. For a room of 20 m2For example, 2000 W of thermal power is needed, here it is worth adding 20% of the reserve, we get 2400 W. This thermal power is provided by one or two radiators, if there are two windows in the room - under each window. According to the table, we see that pipes with an internal diameter of 8 mm are needed to cover this power, but 10 mm is also suitable. Of course, these are all conditional calculations, but they will help to navigate the budget for the purchase of pipes.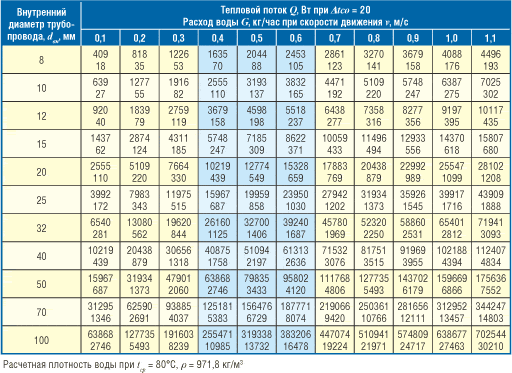
Finally, we note that it is better not to save on heating pipes - this will save from numerous problems. The products of such manufacturers as Akwatherm, Rehau, Banninger, Wefatherm, FV-Plast have proven themselves excellently.