6 tips for cold galvanizing metal
For all their strength, metal products have one significant drawback - they rust easily. In production conditions, steel products protect against corrosion by hot dip galvanizing. This is a rather complicated and expensive process, in addition, it is not designed to protect large structures. In the home for rust protection the roof, the fence, visor, automobile and other constructions it is best to use cold galvanizing of metal, which is carried out using special zinc-containing compounds. The coating process is as simple as possible, and the method of cold galvanizing for many reasons can be called universal. We will deal with technology, compositions and find out how the zinc “armor” works.
No. 1. General principles of cold galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing protects the metal from corrosion for the next 40-50 years, and no additional measures are required. The technologically complex and costly process in everyday life has been replaced by cold galvanizing, which allows you to get a high-quality protective coating with minimal effort, but it will have to be updated periodically.
The process of cold galvanizing resembles simple staining. metal structures, only instead of ordinary paints use zinc-filled paints (ZNK). They include at least 94% zinc, the rest are binders. ZnK should not be confused with zinc-containing paints: in them the proportion of zinc is lower, and the density of the composition is always less than 2.2 kg / l.
Due to its simplicity, cold galvanizing of metal is carried out not only in industrial conditions, but also at home to protect structures of any size and geometry.
No. 2. The nature of cold galvanizing
To better understand the features and advantages of the method, it is necessary to recall the school chemistry course. The process of protecting iron alloys with zinc possible due to the unique physicochemical properties of this element. Zinc very easily enters into chemical reactions with various types of substances, and when interacting with water forms an practically insoluble hydroxide, which covers the surface of the metal and prevents further interaction of zinc and water. In a similar way, by the way, aluminum behaves.
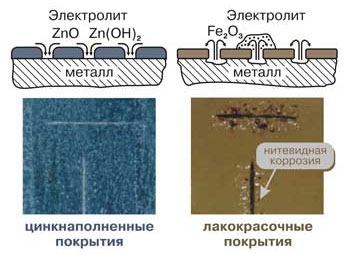
If you coat a steel structure with a layer of zinc, then zinc in the air will begin to oxidize over time. The reaction product is zinc oxide, which does not react with water and forms a strong film on the surface of the structure. That's all, further reaction is not possible on this, since zinc oxide and zinc hydrogen carbonate (formed in a smaller amount) are inert with respect to water. it barrier protection. It is worth noting that iron also reacts with water to form oxides, which we call rust, but these compounds do not form a continuous dense film, passing moisture into the metal and provoking the development of corrosion.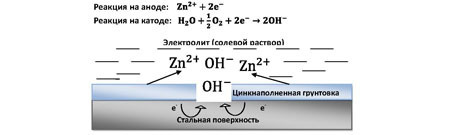
In addition to barrier protection, zinc also provides electrochemical. We recall the electrochemical series of metal stresses, in which zinc stands before iron. This means that zinc is chemically more active and will react first in the zinc / iron pair. In the presence of atmospheric moisture, an electrochemical reaction may occur with the formation of zinc carbonate.This compound is also insoluble in water and stops further development. corrosion process.
The principle of "work" of the zinc coating remains the same, despite method of application:
- hot dip galvanizing;
- electrolytic galvanizing;
- diffuse galvanizing;
- gas-dynamic galvanizing;
- shoping;
- cold galvanizing.

Immediately after the protection of the metal structure by the method of cold galvanizing, mainly electrochemical protection works: until the coating has reached its maximum strength, moisture particles can penetrate through it and reach steel. At this point, an electrochemical zinc / iron pair is formed. In the future, the protection is built on the barrier type, but if the integrity of the paint is violated and moisture penetrates the structure, then the electrochemical protection is activated again.
No. 3. Advantages and disadvantages of cold galvanizing
Cold galvanizing of metal is a simple, reliable and one of the most popular ways to protect it. In everyday life, technology has become widespread, as it has a lot of advantages:
- the compositions used are distinguished by good adhesion both to the base and to decorative paints and varnishes, so the design can easily be painted in the required color;
- it is possible to apply a coating on a product of any size and any geometry, and if it is already installed and operated, then it is unnecessary to dismantle it - all work can be done on site;
- surface preparation before cold galvanizing is relatively simple;
- metal parts protected by this method are easy are welded between themselves;
- ease of coating, no special skills and tools will be needed. For painting use spray guns, paint rollers and ordinary brushes;
- work can be done in almost any weather (permissible air temperature -20 ... + 400FROM);
- low financial and time costs.

The main disadvantage of cold galvanizing - low resistance of the coating to mechanical damage. Simply put, you can simply scratch the paint by exposing the steel structure. On the other hand, updating the coverage is not so difficult and expensive, so the minus can not be called very significant.
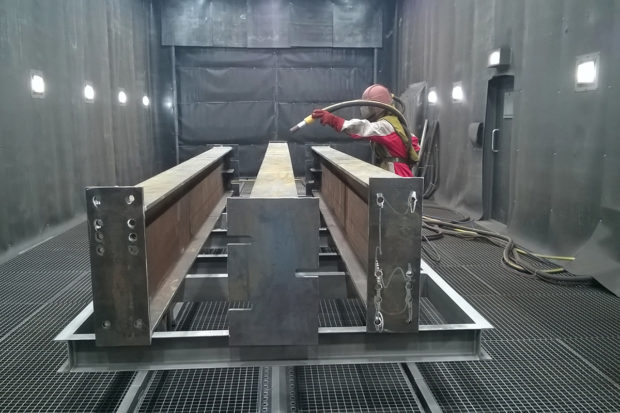
Number 4. How is cold galvanizing carried out?
The method of cold galvanizing is the application of compositions with a zinc content on the metal surface. The technology and application procedure depends on the type of composition, but most often materials are used whose characteristics are specified in GOST 9.305–84. The same document allows the use of cold galvanizing compounds on any structures, with the exception of high strength steels and magnesium alloys.
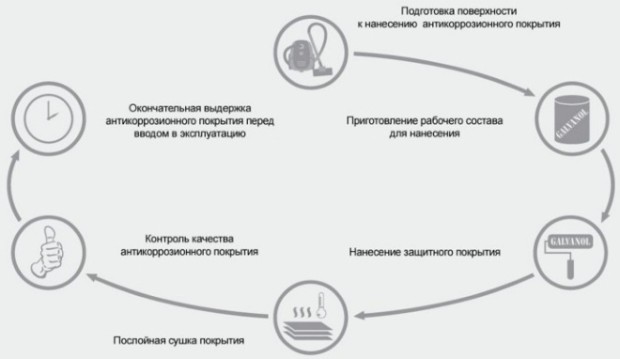
The process of applying the composition (we will talk about the most popular later) is preceded by a thorough metal surface preparation:
- removal of any kind of pollution, salts, coking;
- abrasive surface treatment (abrasive blasting or hydrodynamic method) to give the necessary roughness (provides better adhesion) and remove old rust;
- design drying;
- manual cleaning of splashes, agnails and sharp corners;
- dust removal by a stream of air.

If there are grease stains on the metal, the surface must be degreased. Standards require a thorough check of the level of dust removal, degreasing and roughness, which requires special devices. When it comes to protecting critical construction, this is best not to be neglected.
This is where the preparation ends and begins direct cold galvanizing. It is produced at a surface temperature above the dew point of three degrees or more, and the air temperature recommended by the manufacturer. Apply paint using special equipment (pneumatic, colorful cameras, etc.) in several layers, each new layer is applied after the previous one has dried. For processing some places, you can use a brush and a roller.The coating is allowed to dry, then leveled. You can subsequently apply ordinary paint to it. It is advisable to check the quality of the coating after applying the ZNK and drying it, using special devices that allow you to measure the thickness of the protective film.
To determine the dew point, you should use a hygrometer, thermometer, psychrometer or device that allows you to measure both temperature and humidity. The readings of the devices are compared with the table and determine whether it is possible to carry out the procedure of cold galvanizing of metal.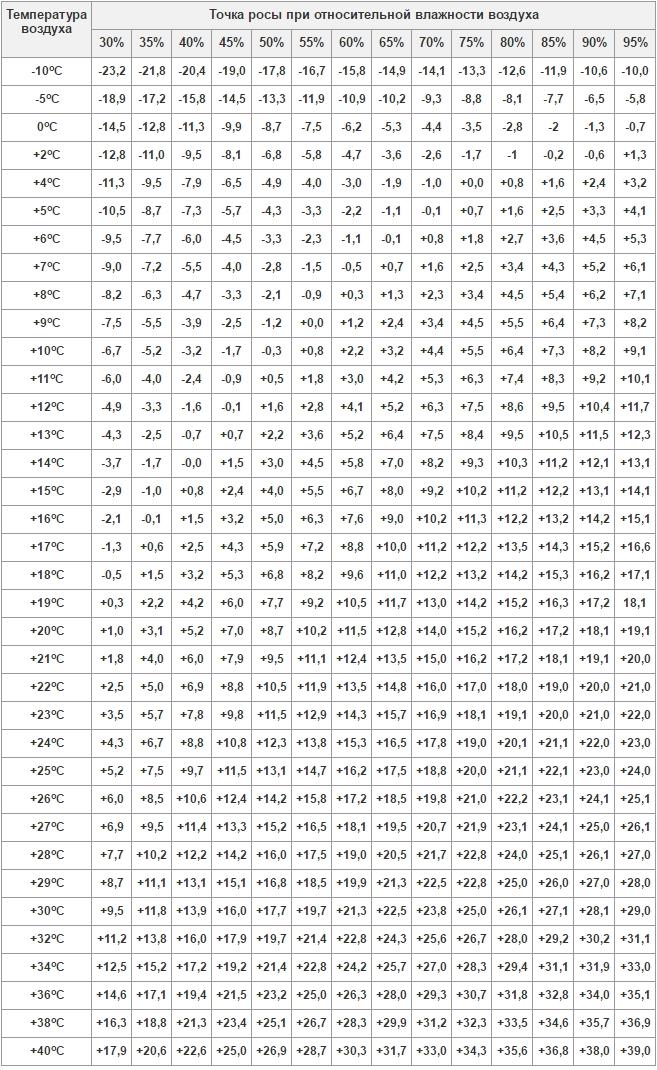
No. 5. Where can I use cold galvanizing?
Cold galvanizing is suitable for any steel except high strength and alloy with a high content of magnesium. There are no requirements for the size, weight, shape, thickness of the products. The method is suitable for already manufactured and installed products (including large metal structures). You do not need to dismantle them.
Galvanization can be used both in production and in the maintenance and repair of infrastructure elements (for example, pipelines, tanks and towers), and in ordinary life for such structures as:
- roofing;
- fences and gates, gates;
- garagesmade of metal;
- underbody and other car body parts;
- fittings;
- various containers and tanks;
- carts, agricultural and construction tools.

No. 6. Cold galvanizing compounds
According to the standards, at least 94% of zinc with a particle size of 12-15 microns or 88% of zinc with particles of 3-5 microns should be contained in the CSC. The higher the zinc content, the better the anti-corrosion properties will be, and the finer the particles, the better the adhesion. There are many cold galvanizing compoundsbut we will focus on the most popular:
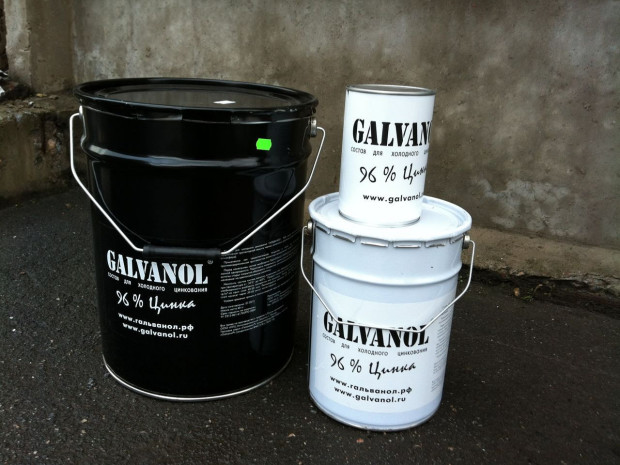
- "Galvanol" - composition based on pure electrolytic zinc and with a low content of binding components, domestic development. The composition provides excellent adhesion and can be applied even to rusty structures, if the rust on them holds well. It is applied quickly and easily, can be used at temperatures from -30 to +500C, as well as with high humidity. The composition is resistant to salt and alcohol solutions, and the finished coating is resistant to abrasion and impact, has good adhesion to paints. It is available ready for use, can be applied by brush, roller, spray, aerosol spray. The scope is widest;

- Tsinotan It is used as an independent anti-corrosion agent and in combination with other compounds. It can be used in any climatic conditions, it is often used in industry to protect structures in salt water or polluted atmosphere. The composition covers fences, tanks for petroleum products, power transmission towers, pipes, automobile structures, etc. It is used by giants of domestic industry;
- Zincolol - polyurethane primer with a high content of zinc, very flexible, resistant to high temperatures, salt water, oils, oil and alkalis;
- Zinol - the composition includes zinc particles of different fractions ranging in size from 4 to 20 microns or more, is applied with a thickness of 100-120 microns, dries in 1 hour, has a high resistance to water;
- CEEC contains zinc powder and ethyl silicate, well suited for high alloy and ordinary steels;
- Master AK-100 Great for car bodywork;
- UR-100 Liquid Zinc produced on the basis of zinc powder with a particle size of 3-5 microns, is inexpensive;
- Zinga - composition for cold galvanizing of metal from the Belgian company Zinga Metall. The manufacturer uses 3-5 micron zinc powder and claims the unique properties of his product, which explains the high cost, almost equivalent to hot dip galvanizing.
 It is important that the processed product is not subjected to constant mechanical stress - in this case, the coating will not last very long.
It is important that the processed product is not subjected to constant mechanical stress - in this case, the coating will not last very long.
Cold galvanizing is suitable for any product that needs to be protected against corrosion. Despite the fact that such a coating can be damaged, like ordinary paint, it works efficiently and eliminates the appearance of rust stains, and also simplifies painting: paint on the zinc layer adheres better than on conventional metal.