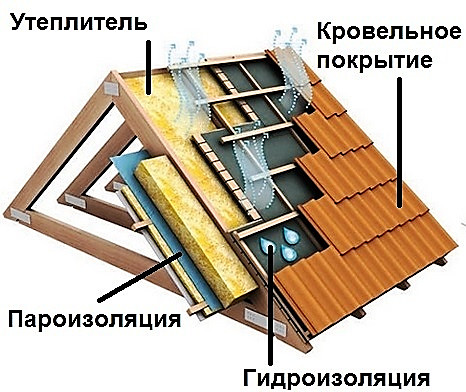
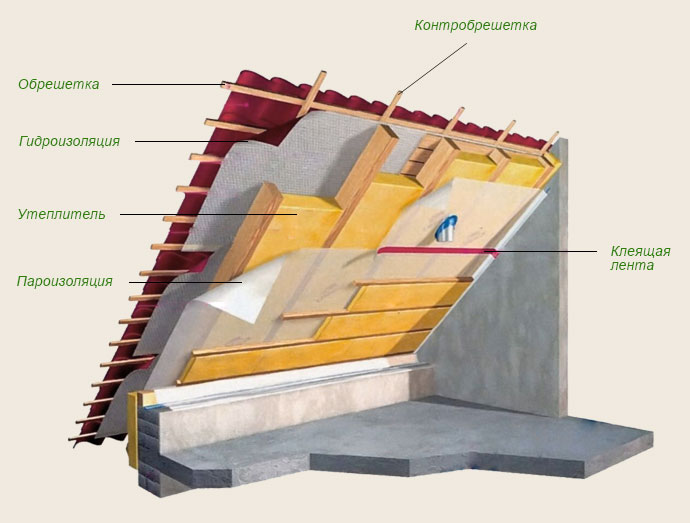
8 tips for choosing a heater for the attic
The attic can serve not only as a storage place for all necessary and unnecessary things - there you can equip a bedroom, living room, nursery, study or even a bathroom. To make the room under the roof comfortable, it’s not enough to make repairs there and put powerful heaters, - you need to take care of quality insulation. Attic - One of the coldest places in the house, because on the top and at least on both sides it borders the street, and the slopes of the roof here play the role of not only the ceiling, but also the walls. If you do not insulate the attic, then no heater will help to create normal living conditions there, and all the heat will easily go outside. So what kind of insulation for the attic is better to choose than to insulate the walls and roof and what thickness should the insulation be?
No. 1. What should be the insulation for the attic?
Not every heat-insulating material is suitable for warming the attic, since this is a rather specific room. High-quality insulation should have such characteristics:
- low thermal conductivity Is the most obvious requirement. The material should reliably protect the room from the cold, while keeping the maximum heat inside. Moreover, heat insulator must withstand temperature extremes, be durable, not crack and do not lose its integrity over time;
- soundproofing properties should be higher, the more “loud” roofing material is selected. Metal tile and corrugated board, for example, during rain and hail they make an unpleasant sonorous sound, and high-quality soundproofing able to significantly reduce discomfort;

- moisture resistance. It is advisable to choose a material that is inert to moisture and does not accumulate it, because with water absorption, the weight of the insulation increases (therefore, the load on all structures increases) and its thermal insulation qualities decrease. If the material is suitable for all other parameters, but prone to moisture accumulation, it is better to use hydro and vapor barrier together with it - this will complicate the installation, but will make the insulation more durable;
- fire resistance, especially if the roof frame is made of wood. For maximum flame resistance, even some flame retardant materials are treated with flame retardants - substances that prevent the spread of fire;
- resistance to fungus, mold and rodents;
- environmental friendliness;
- profitability;
- ease of installation will be a plus, but it is impossible to apply some very effective spray-type heat insulators with your own hands.

To warm the attic today use mineral wool, extruded polystyrene foam, ecowool, polyurethane foam and some other heat insulators. It is not recommended to use a charge heat insulator (for example, expanded clay), since it will need a lot to achieve the necessary thermal insulation qualities. In the mountainous Caucasian regions, even wool - in terms of thermal insulation properties, it is close to mineral wool, but is subject to the negative effects of insects and rodents.
No. 2. Mineral wool for attic insulation
Mineral wool can be safely called one of the most popular heat-insulating materials, and if we talk about the insulation of the attic, then you can safely give it the palm. It is worth remembering that mineral wool is different, and its properties differ depending on the raw materials used: slag produced from blast furnace wastes, stone wool - from rocks, most often from basalt (therefore, the name was also fixed to it basalt wool), glass wool - from glass waste or silicon-containing rocks. Slag wool is practically not used in private construction, glass wool is used, but not often, and stone wool is most widely used, therefore, it is usually understood as mineral wool.
Stone (basalt) cotton wool for the attic
Stone wool due to its fibrous structure has a number of undeniable the benefits:
- excellent thermal insulation properties, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material is approximately 0.035-0.045 W / m • K;
- excellent noise insulation qualities, so if you plan to equip a nursery or bedroom on the attic floor, this is a great option;
- fire resistance. The material calmly tolerates heating up to 550-6000C and more, because it is based on stone;
- convenience in work. It is not difficult to install slab or roll mineral wool, and there is no need to use special protective equipment - the material does not include sharp fibers, which are so dangerous when working with glass wool;
- resistance to mold;
- good vapor permeability;
- low price.

Among cons:
- the ability to absorb moisture, therefore the arrangement is reliable waterproofing it is strictly necessary, which complicates the work;
- rodents can settle in mineral wool, which, of course, will not have a very good effect on thermal insulation. Mice don't live only in a layer expanded clay insulation, foamglass and polyurethane foam, therefore, in other cases, it is necessary to carefully close the technological holes and take measures to eliminate rodents.
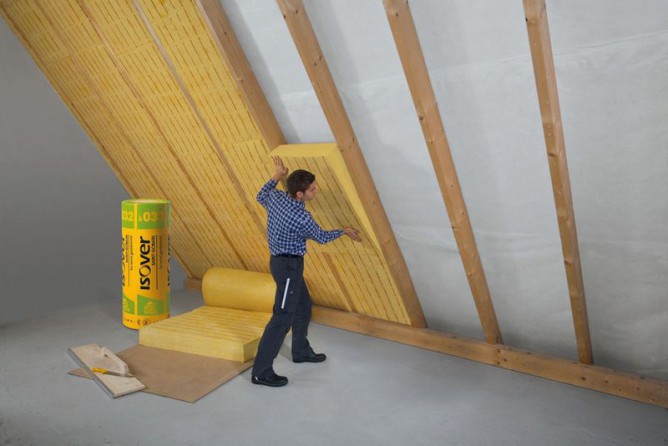
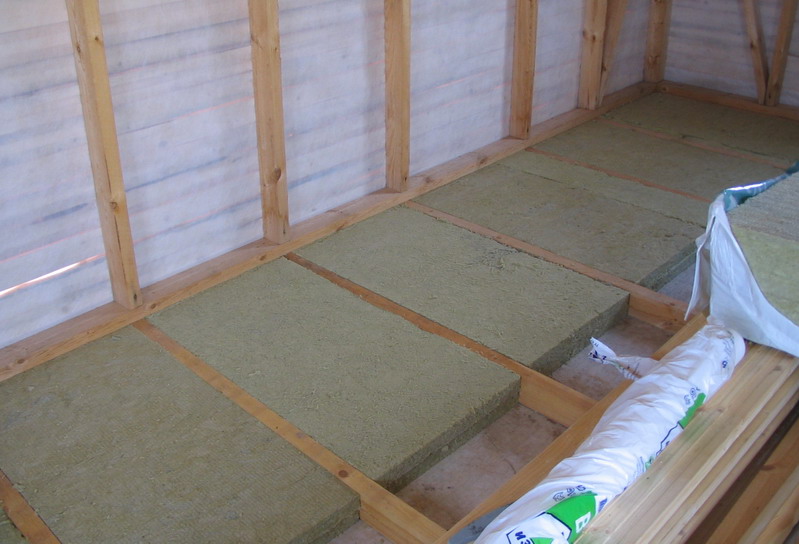
Stone wool is available in the format plates and rolls. To warm the inclined walls of the attic, plate material is better: it will need to be cut and inserted into the holes between the beams of the ceiling. Roll material is not so durable and is better suited for insulating horizontal surfaces. Recommended use two-layer mineral wool insulation: Slabs are placed between the rafters, and roll material is fastened on top of them. Thus, it is possible to minimize the risk of cold bridges. Separately, it is worth noting the loose basalt insulation: it is suitable for the most inaccessible places, but it is applied using special equipment.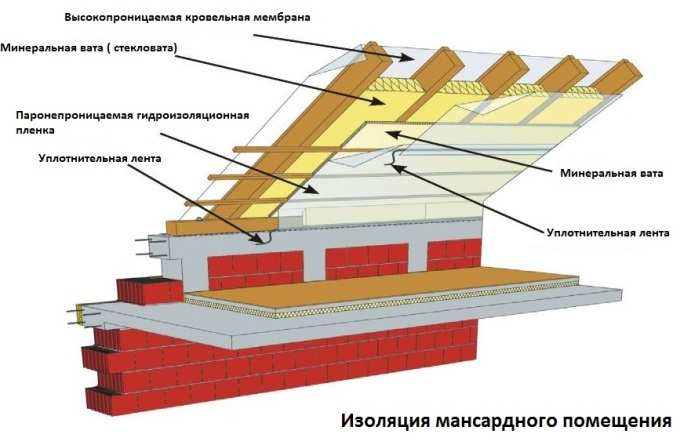
Glass wool
Glass wool is cheaper than stone wool, but is used infrequently due to inconvenience. Since the material is made from glass waste, it contains small, pointed particles that can easily injure the skin and respiratory tract. However, if you work with glass wool in compliance with all the rules of personal protection, then you can inexpensively and efficiently insulate the attic. To the main the benefits Material include:
- excellent heat and sound insulation properties. Thermal conductivity coefficient 0,030-0,052 W / m · K;
- high strength and resilience;
- fire resistance. Glass wool withstands heat up to 4500C without changing properties;
- low price.

No. 3. Polyfoam for attic insulation
Familiar to all of us Styrofoam several decades ago was one of the most popular heaters used in private construction. Today it is used less and less, and among the main the benefits, which make it possible to consider polystyrene as one of the possible insulation for the attic, it is worth highlighting:
- very low price;
- light weight;
- ease of installation;
- good soundproofing properties;
- quite high durability.
Cons significantly more: it is fragility, and the ability to accumulate moisture, and a high risk that rodents will live and breed in such a heater. To negate all these shortcomings, you will need serious protection of the material, the arrangement of which practically negates the benefits of a low price, therefore today in construction more and more often use a more advanced analogue - extruded polystyrene foam.
Number 4. Extruded polystyrene foam for attic insulation
Extruded polystyrene is catching on mineral wool in popularity. In terms of chemical composition, this is the same ordinary polystyrene foam, but only a fundamentally different production technology allows one to obtain material with more favorable operational qualities. The thing is that regular foam obtained by increasing the microbeads under the influence of steam, and extrudedas the name suggests, by extrusion at elevated temperature and pressure, as well as by the addition of blowing agent.
The main advantages:
- high-quality thermal insulation. The coefficient of thermal conductivity at the level of 0.029-0.034 W / m · K;
- moisture resistance, which is largely ensured by the structure of the material with closed pores;
- ease of installation, which is ensured by low weight and ease of processing;
- sufficient strength;
- low price;
- resistance to mold and rodents.
Among cons not the highest vapor permeability, so you have to take a more responsible approach to ventilation organization attic room, as well as low resistance to burning. To insulate the attic, it is better to take polystyrene foam of the G3 combustibility class - according to the norms, it can be used even in rooms with increased fire safety requirements. Since the material belongs to tile insulation, a cold bridge may form at the joints of individual plates, so it is better to take polystyrene foam with a special lock.
No. 5. Polyurethane foam for warming the attic
Sprayed polyurethane foam in terms of heat-insulating qualities it is considered one of the most effective heaters - a layer of 2.5 cm is identical to a layer of mineral wool of 8 cm. The material is applied by special installations in liquid form, as a result of the interaction of two components of the mixture, the necessary polymer and carbon dioxide are obtained. Hardening is fast.
The main advantages:
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of 0.02 W / m · K, and this is one of the best results;
- the ability to create a completely seamless surface, so the problem of cold bridges will be completely solved;
- absolute moisture resistance, which is important for the material to be used under the roof itself;
- high adhesion to most materials;
- the ability to insulate the attic of the most complex form - in some cases, the use of stove insulation is generally inappropriate, and the foam makes it easy to fill all cracks and inaccessible places;
- high vapor permeability;
- resistance to mold and rodents;
- high speed of work.
Among cons the price and the need to resort to the help of professionals, but all the work will be carried out very quickly. In addition, the ignition temperature of the material is not very high - about 200-2150C, and when burning, the material emits toxic gases.
No. 6. Foam glass for warming the attic
Foam glass in terms of the totality of qualities, it can be considered almost an ideal insulation material, but the material was not widely used - it's all to blame high price. It is produced, like glass wool, from waste from the glass industry, but the technology is completely different: a blowing agent is added to the glass powder and heated at very high temperatures. Under such conditions, melting and swelling occurs, and as a result we get silicate glass with a huge number of bubbles. This structure allows us to talk about numerous the benefits material:
- good heat and sound insulation. The thermal conductivity is about 0.045 W / m · K and does not change over time;
- high durability. Manufacturers say that the material will last about 100 years without significant changes in its properties;
- resistance to mold and fungus;
- high strength;
- resistance to temperature extremes and high temperatures, fire resistance;
- moisture resistance and high vapor permeability.
Due to the high price of the attic, foamglass is infrequently insulated.
Number 7. Ecowool for attic insulation
Ecowool produced on the basis of recycled cardboard and paper with the addition of boric acid as an antiseptic and sodium tetrabortate to reduce flammability and impart insecticidal properties to the material.
The main advantages:
- good heat-insulating qualities, thermal conductivity coefficient 0.04 W / m · K;
- good soundproof qualities;
- fire safety, but at high temperatures the material may begin to smolder;
- moisture resistance;
- resistance to mold, fungus and rodents due to the additives used;
- vapor permeability;
- low cost;
- the best results can be achieved by using a sprayed ecowool that perfectly fills all cracks and bumps.
disadvantages:
- special installations and professionals who know all the features of the process are needed for spraying ecowool;
- Ecowool may decrease over time in volume, but if the installation was performed correctly and in compliance with all the nuances, then the shrinkage will be minimal.

Number 8. Calculation of insulation thickness
It is better to calculate the required insulation layer separately for coating, walls and attic floors, since the normalized heat transfer resistance is different for them. The last parameter, ideally, can also be calculated independently, using data on the minimum temperatures, duration of the cold period and comfortable temperature in the house. You can use the already calculated average values of the normalized heat transfer resistance for large cities, given in the table.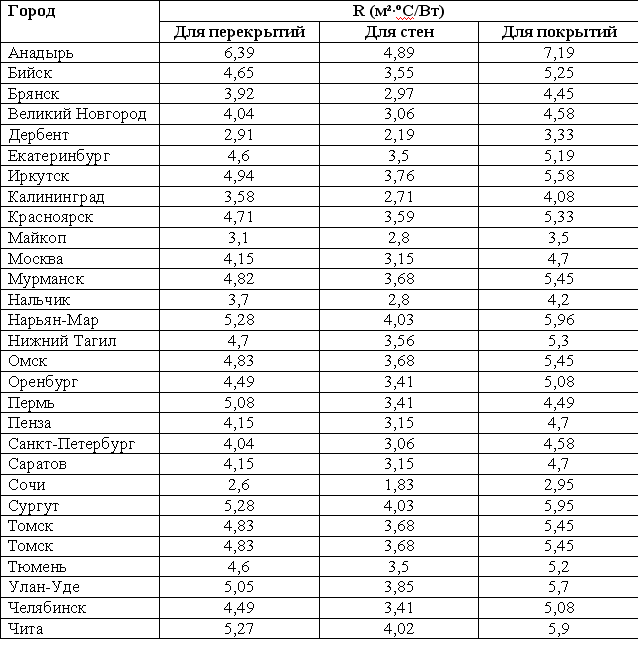
When calculating, it is worth considering the heat transfer resistance of all elements of the fence, including the walls of the gables and the roofing pie. It is convenient to use special calculators for this or even turn to professionals. With a certain degree of error, it is possible to make a calculation, taking into account the necessary heat transfer resistance of only the roof of the attic, because it occupies the largest area among all the external fences of this room. According to the rules, the heat transfer resistance of already existing materials is taken away from the tabular or independently calculated value, but for the roofing pie this value is very small, therefore it is neglected.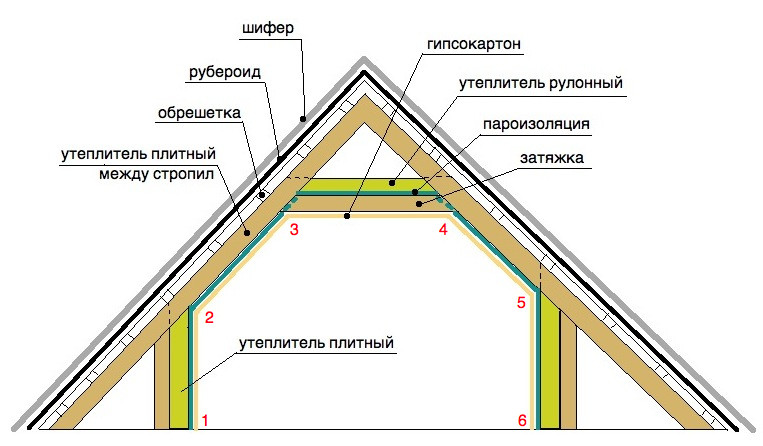
It turns out, for insulation with mineral wool (0.035-0.045 W / m * K) of the attic in Moscow (heat transfer resistance 4.7 m2K / m) a heat insulation layer of 16.5-21 cm is required, depending on the characteristics of the cotton wool, the thermal conductivity index is always indicated on the package. Specialists recommend in this case to make thermal insulation with plates 20 cm thick, and on top to mount rolled mineral wool another 5 cm thick.
Naturally, the attic room is already insulated from the inside, and the practice of combining two types of insulation is widespread. Properly executed thermal insulation allows you to use the attic all year round and turn it into a full-fledged living space.