8 tips for choosing polycarbonate for a greenhouse
The advent of polycarbonate has greatly simplified the life of summer residents and owners of large agricultural companies. This material surpasses its closest competitors in many ways, plastic wrap and glass, but expanding its assortment made it difficult to choose and increased the risk of buying a low-quality product. Today, those who build a greenhouse with their own hands, and those who prefer to buy a finished structure, are equally concerned about the question of how to choose polycarbonate for a greenhouse so that the material lasts more than one year and provides normal conditions inside the structure. Looking ahead, we note that it is worth considering a lot of nuances, but a careful approach will be rewarded with high durability of the greenhouse and minimal repair costs.
No. 1. The main advantages of polycarbonate
Why is this relatively new material instantly conquered summer residents throughout the country and with leaps and bounds displaces film and glass from sites? Reasons for popularity are worth looking at material structure features. On an industrial scale, polycarbonate began to be produced in the 60s of the last century, it was used in many fields of construction and industry, and material suitable for greenhouses appeared a bit later with the filing of Israeli scientists.
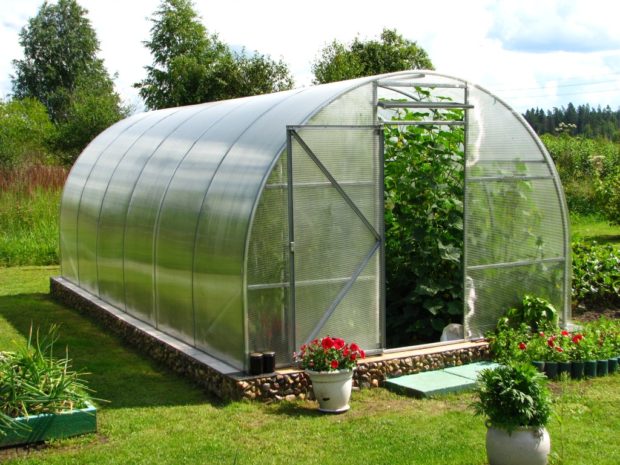
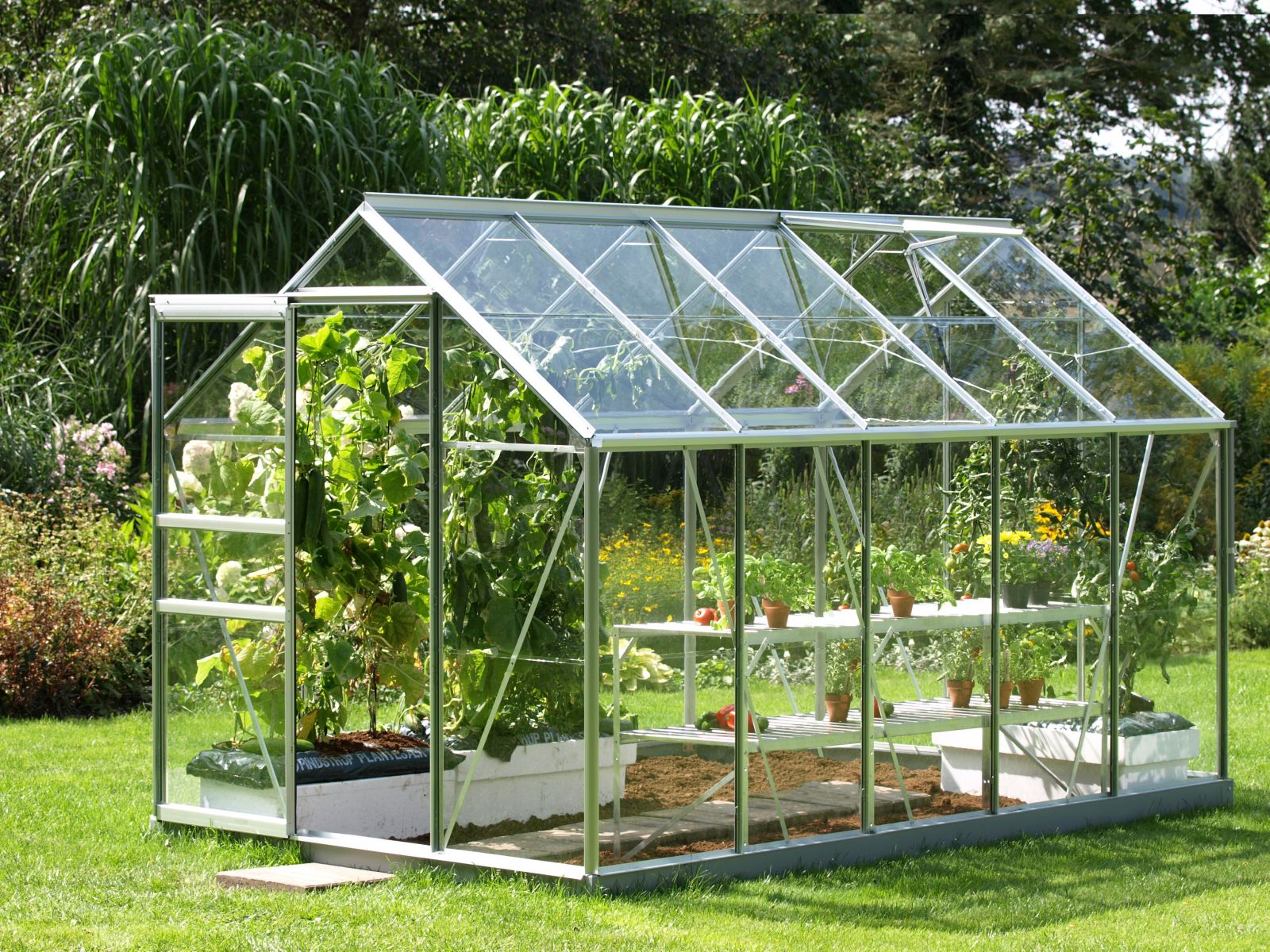
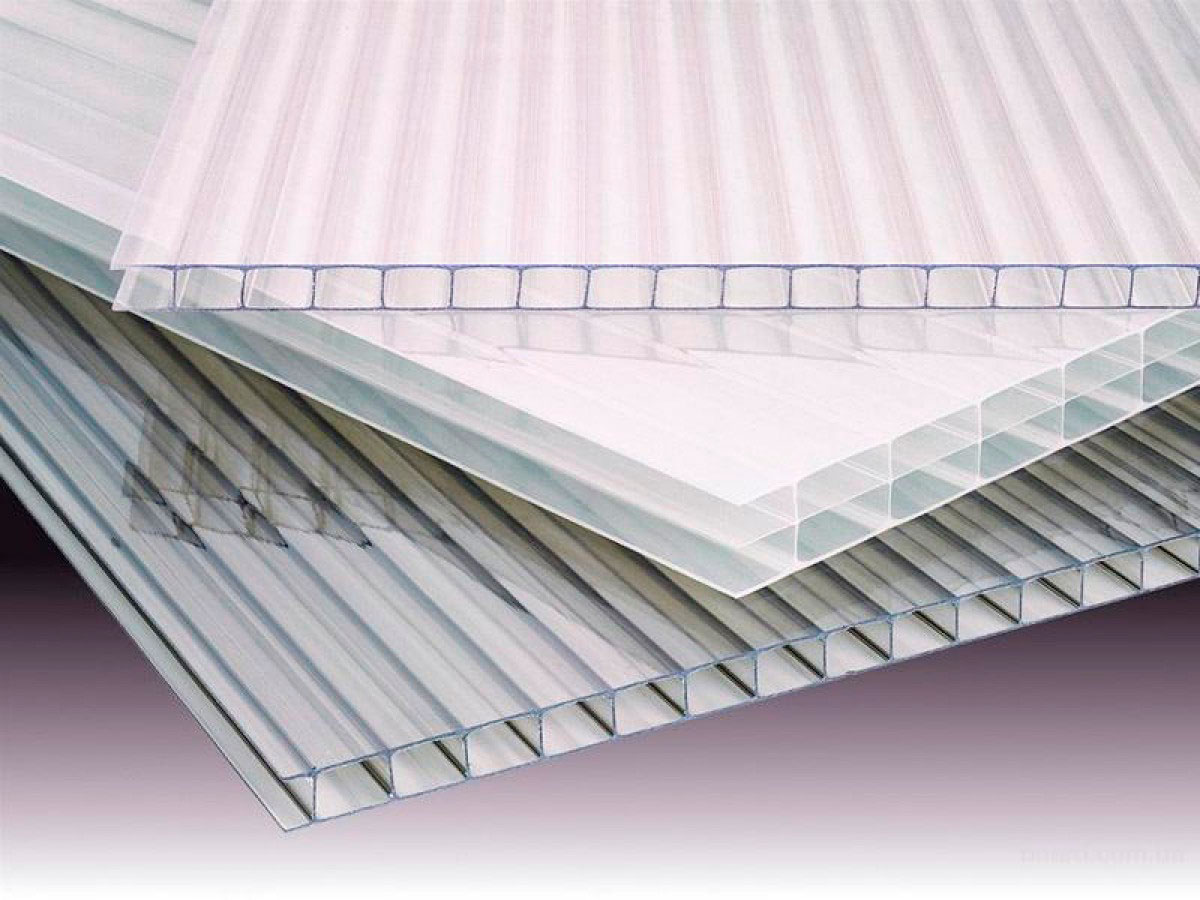
For arrangement of greenhouses use cellular polycarbonate only - monolithic analogue is heavier, does not have sufficient strength and heat insulating qualities. The material is two or three plates parallel to each other, connected by jumpers. The latter play the role of stiffeners, and the space between them, filled with air, increases the thermal insulation properties of the material. The sheet structure can be single-chamber, two-chamber, etc.
The main advantages of cellular polycarbonate for greenhouses:
- excellent transparency and ability scatter the sun. Through colorless polycarbonate, up to 92% of the sun's rays pass, which positively affects the crops grown. Moreover, the material with a special protective film allows you to protect plants from harmful ultraviolet radiation harmful to them;
- light weight. This parameter depends on the thickness of the sheet, but even the thickest material will weigh several times less than the glass analog, which reduces the load on the frame of the greenhouse;
- flexibility and plasticity. Cellular polycarbonate during installation can be bent, creating arched greenhouses;
- not bad mechanical strength. From the impact, the material will not tear like a film, and will not break into fragments like glass. The thicker the polycarbonate selected, the more difficult it will be to break its integrity;
- excellent thermal insulation qualitiesexplained by the honeycomb structure of the material. The cost of heating can be minimized. Soundproofing qualities material is also at altitude - on average, it can reduce noise by 22 dB;
- resistance to temperature extremeswinds moldto the fire.

Durability high-quality polycarbonate exceeds 10 years, and bona fide manufacturers give a guarantee of up to 15 years. Among cons the material is unstable to sunlight, like any plastic, but thanks to a special film coating, this minus was also eliminated. Cellular polycarbonate has no other significant shortcomings, especially in comparison with other covering materials for greenhouses - the main thing is to buy high-quality material, and not a handicraft.
Typically, cellular polycarbonate is produced in sheets of dimensions 2.1 * 6 m and 2.1 * 12 m, less often 2.1 * 2 m, but the thickness can fluctuate over a wider range (3.5-16 mm), and it is from for the most part, the basic parameters of the material depend on it.
No. 2. Choose the thickness of cellular polycarbonate
Thickness is a determining factor when choosing polycarbonate for a greenhouse. In this matter it is important consider a lot of factors and choose a material that is not too thin, but not too thick: in the first case, the strength decreases, in the second - the light transmission decreases.
The main factors that affect the choice of polycarbonate thickness:
- climate of the region, in particular, the height of the snow cover and its weight, which determines the maximum load on the material;
- wind load in the region;
- frame material. The metal frame has a better bearing capacity and is able to withstand a higher load than a wooden one;
- crate pitch. The closer the frame elements of the greenhouse are located to each other, the more durable the structure will be and the less thick polycarbonate may be needed;
- seasonality of use. If the greenhouse will be operated only in the autumn-spring period, then polycarbonate can be selected thinner. For year-round greenhouses, the material is chosen significantly thicker, because it must withstand not only snow and wind, but also retain heat;
- type of construction. If you plan to build an arched, domed or drop-shaped greenhouse, you need to think in advance whether polycarbonate can be bent in a certain way. The thinner the material, the higher the bending radius.
How to choose the optimal thickness, taking into account all these factors? To get the most accurate value, you can contact the professionals. The second option is to buy finished greenhouse, the polycarbonate of optimum thickness is already included in the package (type of construction and climatic features are taken into account). An alternative solution is to try to choose the necessary polycarbonate on your own: complex calculations will not be needed, since you can be guided by the practice of using the material, the main parameters of polycarbonate sheets of different thicknesses (in the table below) and regional climate data, which are also easy to get on the network.
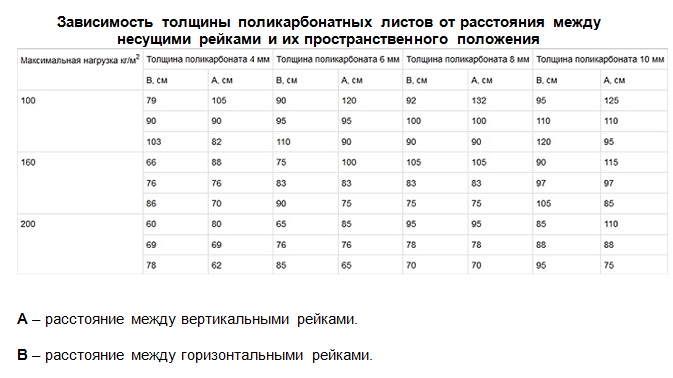 Considering different options for the thickness of polycarbonate for your greenhouse, it does not interfere be guided by the following recommendations:
Considering different options for the thickness of polycarbonate for your greenhouse, it does not interfere be guided by the following recommendations:
- polycarbonate with 4 mm thick, but it should still be attributed to the economy option. It makes sense to use it only in seasonal greenhouses, otherwise even a small step of the crate (0.5 m) will not save from deformation under the weight of snow. Trying to save on polycarbonate, you have to spend money on reinforcing the frame, and in this case, the design only becomes more expensive. Do not forget that the frame does not transmit light, and the more frequent the crate, the greater the shadow on the plants. Although it’s not so scary for small household greenhouses, but on a production scale this is already a serious minus, because reducing the amount of lighting by 1% reduces the yield by exactly the same amount;
- for most regions of the country, the optimal thickness of polycarbonate for the construction of spring-autumn greenhouses is called 6 mm, and for winter greenhouses - a single chamber sheet 10 mm thick;
- arched and domed greenhouses snow cover is not so much delayed, which means that less load is applied to polycarbonate.Nevertheless, it is unreasonable to choose too thin material for arched greenhouses - at the time of a sharp cooling after a thaw, a layer of ice forms on the surface of the greenhouse on which snow will hold well;
- too thick polycarbonate it is also undesirable to use, because along with an increase in strength and thermal insulation qualities, the ability to transmit light decreases, as well as the weight increases, so strengthening the structure will be necessary. Through polycarbonate with a thickness of more than 10 mm passes 25-50% of sunlight, and this is the loss of yield and waste on artificial lighting, so in private greenhouses it is not recommended to use material with a thickness of more than 10 mm.
If the greenhouse is built on its own, then it is better to determine the thickness of the polycarbonate at the design stage.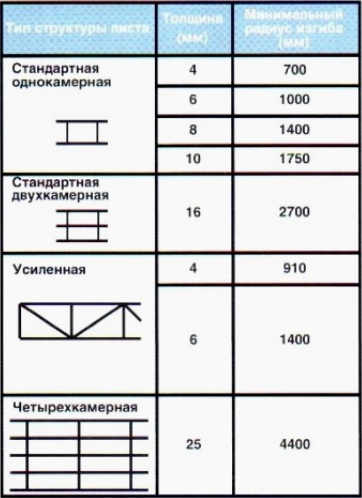
No. 3. Cell geometry and polycarbonate strength
Partitions inside the polycarbonate form a honeycomb, the shape of which significantly affects the strength of the material and its load-bearing capacity. The most common options are:
- rectangular honeycombs - the most common material. The bearing capacity is not very high, but the light transmission is maintained at a high level. Such polycarbonate is recommended for use in those greenhouses where artificial lighting is not provided;
- square honeycombs make the material more durable and suitable for the construction of medium-loaded greenhouses;
- hexagonal honeycombs allow to achieve the highest strength, but greatly reduce the level of light transmission, therefore, for the construction of greenhouses such polycarbonate is used infrequently, and if applicable, it requires mandatory arrangement artificial lighting.

Number 4. Polycarbonate color
Having decided on the required thickness of the material and coming to the store, you can find that polycarbonate is available in a whole range of colors. Which one is better? Of course, transparent, because it allows you to provide plants as close as possible to natural lighting, and besides, it allows maximum sunlight. Summer residents who want to get the maximum yield and not spend money on additional lighting, choose transparent polycarbonate.
Painted polycarbonate is not able to provide plants with a sufficient level of light: bronze, opal, yellow and green sheets transmit only 40-60% of the light, so it’s difficult to talk about normal crops. Some summer residents choose red and orange polycarbonate, citing the fact that the most useful for plant growth is the orange and red range of solar radiation. It is difficult to argue with this statement if we recall the school course in biology and physics, but there is one “but”: fewer useful rays, and their number will not be enough for the normal growth of most cultures, therefore the best choice is transparent polycarbonate.
No. 5. UV protection for polycarbonate
Reading about the positive properties of polycarbonate, you might think that this is an ideal material that does not have disadvantages. Naturally, this is not so. The main minus is the addiction destruction under ultraviolet raysthat start the process of photoelectric destruction on the surface, leading to the formation of small cracks. Gradually, they grow, causing fragility of the panels and their destruction. That is why the material needs additional protection. Hard ultraviolet (in the spectrum up to 280 nm) is harmful to plants, so the protective coating protects not only polycarbonate, but also the crops grown.
Responsible manufacturers use to protect the material special filmapplied coextrusion methodTherefore, during operation it does not exfoliate. Such high-quality polycarbonate can easily last about 10 years. On sale there is a material on which a protective film is applied on both sides, but for greenhouses its use does not make sense. When mounting sheets, it is important to pay attention to the marking and install polycarbonate with a protective layer outward.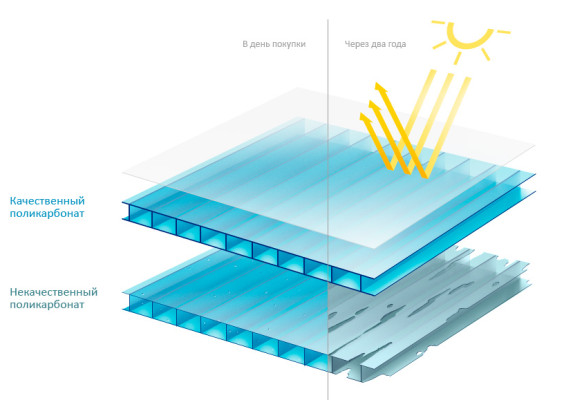
Unscrupulous manufacturers (often Chinese) produce polycarbonate without a protective coating at all, or make it symbolic. It is understood that instead of using a film, the simplest additives are introduced into the mass, which should protect the material from solar radiation. Such polycarbonate "lives" for a maximum of 2-3 years, then it will have to be changed, and this again is a waste. Buying initially cheap material, you should think about the consequences three times. Information on the presence of a protective coating should be indicated on the package and in the accompanying documentation, since it is impossible to examine it externally (the thickness is 0.0035-0.006 mm).
No. 6. What does the prefix “light” mean in the polycarbonate marking?
Tricky manufacturers and sellers sometimes mislead buyers by using the designation “light”. To choose such polycarbonate for a greenhouse means to overpay and get material with reduced strength. Often, thinner polycarbonate is sold under the light version, but the price remains standard. Instead of 4 mm it can supply material with a thickness of 3.5 mm, instead of 6 mm - 5.5, 8 mm - 7.5 mm, etc. It seems that the difference is small, but with a decrease in thickness (which means strength and durability), the price does not fall - not the most profitable purchase. In addition, it is not recommended to take polycarbonate for a greenhouse with a thickness of less than 4 mm.
Number 7. Polycarbonate sheets size and material handling features
With a width of 2.1 m, polycarbonate sheets are sold mainly in lengths of 6 and 12 m, a deviation of 3 mm in width and 10 mm in length is allowed. The accumulated experience of many summer residents makes it possible to form a number of tips for the most rational use of material:
- if the greenhouse has an arched shape, then the length of the arches of the power structures is recommended to be 6 and 12 m in order to avoid transverse joints;
- the distance between the supporting elements of the frame is better done so that the joints of the sheets fall on the profile, which increases the strength of the structure;
- during the construction of double-pitch greenhouses it is better to make the walls and the roof such that the polycarbonate sheets are divided without residues.
Polycarbonate increases in size in heat, and decreases in cold. An increase in temperature by every degree causes the material to expand by 0.065 mm / m. This should be taken into account when attaching polycarbonate to the frame, leaving small gaps between the sheet of material and the supporting structure.
Caring for polycarbonate is as simple as possible: it must be washed several times a year, you can use a mild soap solution, but not aggressive agents. The main goal of this care is to maintain a high level of transparency.
Number 8. Polycarbonate manufacturers: who can be trusted?
To choose the right polycarbonate and in the future count on its durability, it is important pay attention to the manufacturer: fame of his name and duration guarantees (the longer, the better, ideally 10-15 years). When buying does not bother to pay attention to certificates, and it is not recommended to go to the market for polycarbonate - they hardly adhere to the necessary storage conditions.
The products of such companies have proven themselves in the best way:
 Bayer Material Science - A large German concern working in the field of healthcare, agriculture and high-tech materials. Polycarbonate is produced under the brand name Makrolon, has the highest quality, because the main thing for the company is innovation and its own reputation;
Bayer Material Science - A large German concern working in the field of healthcare, agriculture and high-tech materials. Polycarbonate is produced under the brand name Makrolon, has the highest quality, because the main thing for the company is innovation and its own reputation;- Sabic Innovative Plastics - A company located in Saudi Arabia produces polycarbonate of several series under the Lexan brand name. The company has always played a critical role in the development and production of new types of polymers. Today the company’s representative offices and enterprises operate in 40 countries of the world, the range of products is constantly growing;
- Samyang - A Korean company that produces sufficiently high-quality material under the Trirex trademark.In terms of price and quality, this is a good option, so the products are in great demand among domestic buyers;
- Teijin limited - A Japanese corporation that also constantly carries out new developments and offers increasingly advanced polymers. The polycarbonate of the company is very high-quality and durable, but is represented in the domestic market a little;
- Dow chemical - American manufacturer of polycarbonate Caliber and Magnum ABC. The products are of the highest quality, excellent geometry, good durability, but are expensive and have little market presence;
- Polygal - A Russian-Israeli company that produces polycarbonate under the same name. It is a relatively inexpensive material with a long service life;
 Carboglass - A large domestic manufacturer, which gives a guarantee on products for 15 years, and this inspires confidence. At the same time, the cost of the material is lower than for foreign samples, which ensures the popularity of products;
Carboglass - A large domestic manufacturer, which gives a guarantee on products for 15 years, and this inspires confidence. At the same time, the cost of the material is lower than for foreign samples, which ensures the popularity of products;- Safplast innovative - Another domestic company. It produces polycarbonate under the brand name Novattro, gives it a 14-year warranty, while the products are slightly cheaper than Carboglass;
- Plastilux - Chinese manufacturer of polycarbonate Sunnex. Looking in his direction is worth it only if the main criterion for choosing is a low price. Product Warranty 8 years;
- Vizor. Polycarbonate of this brand was previously produced in China, today there are factories in the Czech Republic. Average quality, low price, 5 year warranty;
- ITALON - A Chinese company whose products can be advised to those who want to save as much as possible, since its quality is low and the price is more than budget, a guarantee of 5 years.
It is highly discouraged to purchase material from a no-name company - the consequences of such an act are clear without explanation. Given all the nuances described in the choice of polycarbonate, you can find exactly the material that will be the perfect solution in each case.















Thanks for the review on manufacturers and quality, I’m just going to buy cellular polycarbonate for the greenhouse. Now I know from which manufacturer to look, thanks again!