9 cutting-edge technologies for energy-efficient homes
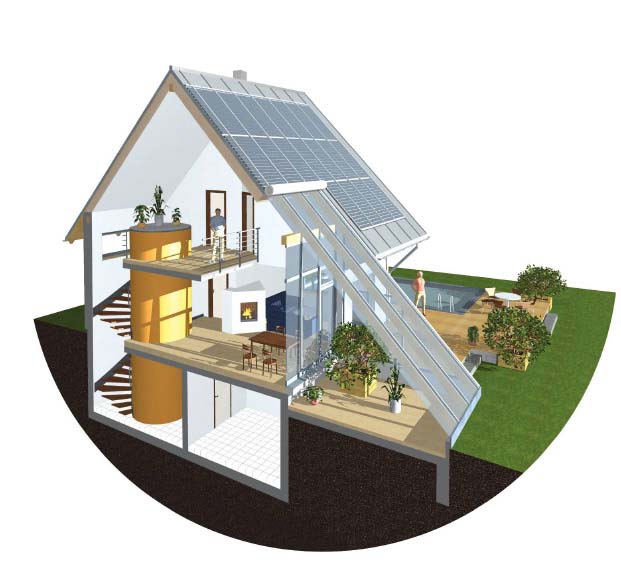
An energy-efficient house is not an idealized view of the house of the future, but today's reality, which is gaining popularity. Energy-conserving, energy-efficient, passive house or eco-house is called today such a dwelling that requires a minimum of costs to maintain comfortable living conditions in it. This is achieved through appropriate decisions in the field of heating, lighting, warming and construction. What technologies for energy-saving houses exist at the moment, and how much resources can they save?
No. 1. Energy Saving Home Design
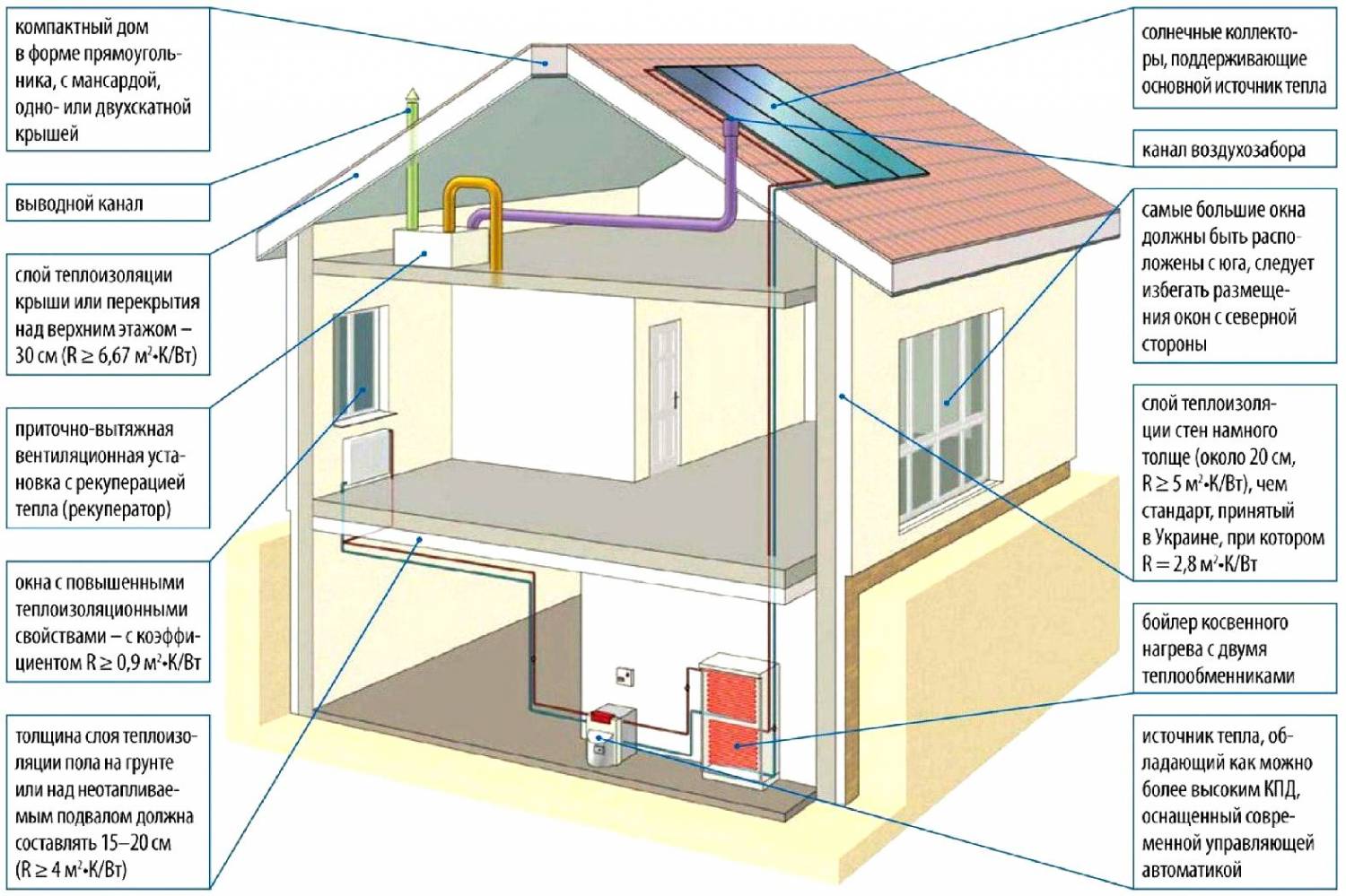
Housing will be as economical as possible if it was designed with all the energy-saving technologies in mind. Remaking an already built house will be more difficult, more expensive, and the expected results will be difficult to achieve. The project is developed by experienced specialists taking into account the requirements of the customer, but it must be remembered that the used set of solutions must be, above all, cost-effective. Important point - taking into account the climatic features of the region.
As a rule, they make energy-saving homes in which they live permanently, so the task of saving heat, maximizing the use of natural light, and so on comes first. The project should take into account individual requirements, but it is better if a passive house is as compact as possible, i.e. cheaper to maintain.
The same requirements can be met various options. Joint decision-making by the best architects, designers and engineers made it possible to create universal energy-efficient frame house. The unique design cooperates in itself all economically advantageous offers:
- thanks to the technology of SIP panels, the structure is highly durable;
- a decent level of thermal and noise insulation, as well as the absence of cold bridges;
- the construction does not require the usual expensive heating system;
- using frame panels, the house is built very quickly and is characterized by a long service life;
- the rooms are compact, comfortable and convenient during their subsequent operation.
Alternatively, you can use aerated concrete blocks for the erection of load-bearing walls, insulating the structure from all sides and getting a large “thermos” as a result. Used frequently wood as the most environmentally friendly material.
No. 2. Architectural solutions for an energy-efficient home
To achieve resource savings, you need to pay attention to the layout and appearance of the house. The house will be as energy-efficient as possible if the following nuances are taken into account:
- correct location. The house can be located in the meridional or latitudinal direction and receive different solar radiation. Northern house is better to build meridionalto cripple the influx of sunlight by 30%. On the contrary, it is better to build southern houses in the latitudinal direction in order to reduce the costs of air conditioning;
- compactness, which in this case is understood as the ratio of the internal and external areas of the house. It should be minimal, and this is achieved due to rejection of bulging rooms and architectural decorations type of bay windows. It turns out that the most economical house is the box;
- thermal buffersthat separate living spaces from contact with the environment. Garages verandas, loggias, basements and non-residential lofts will be an excellent barrier to penetrating cold air from outside;

- proper daylight. Thanks to simple architectural techniques, it is possible to illuminate the house with sunlight during 80% of the entire working time. Premises where the family spends the most time (living room, dining room, children) is better to arrange on the south side, for the pantry, bathrooms, garage and other auxiliary rooms there is enough diffused light, so they can have windows to the north side. East windows in the bedroom in the morning they will provide a charge of energy, and in the evening the rays will not interfere with rest. In the summer in such a bedroom it will be possible to do without artificial light at all. As for window size, then the answer to the question depends on the priorities of each: to save on lighting or heating. Great reception - installation solar tube. It has a diameter of 25-35 cm and a completely mirrored inner surface: taking the sun's rays on the roof of the house, it preserves their intensity at the entrance to the room, where they are scattered through the diffuser. The light turns out so bright that after installation, users often reach for the switch when leaving the room;

- roof. Many architects recommend making roofs as simple as possible for an energy-efficient home. Often they stop at the gable version, and the more gentle it is, the more economical the house will be. On a gently sloping roof, snow will linger, and this is additional insulation in winter.
No. 3. Thermal insulation for an energy-efficient home
Even a house built taking into account all the architectural tricks requires proper insulation to be completely airtight and not to release heat into the environment.
Wall insulation
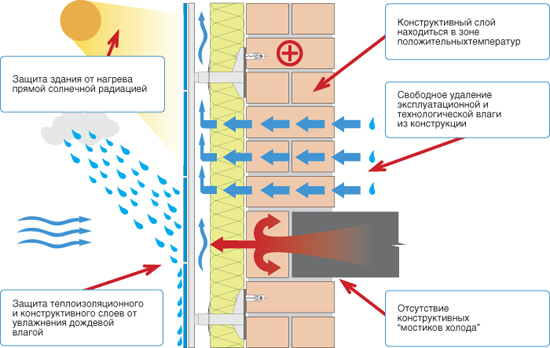
About 40% of the heat from the house leaves through the walls., therefore, their attention is paid to warming. The most common and easiest way of warming is the organization of a multilayer system. Exterior walls of the house sheathed a heater, in the role of which is often mineral wool or expanded polystyrene, a reinforcing mesh is mounted on top, and then - the base and main layer of plaster.
More expensive and progressive technology - ventilated facade. The walls of the house are sheathed with mineral wool plates, and the cladding panels of stone, metal or other materials are mounted on a special frame. Between the insulation layer and the frame there remains a small gap, which plays the role of a “thermal cushion”, does not allow wet insulation and maintains optimal conditions in the home.
In addition, in order to reduce heat loss through the walls, insulating compounds are used in the places where the roof is adjacent, taking into account future shrinkage and changes in the properties of some materials with increasing temperature.
Roof insulation
About 20% of the heat goes through the roof. To insulate the roof using the same materials as for the walls. Widespread today mineral wool and polystyrene foam. Architects advise making roof insulation no thinner than 200 mm, regardless of the type of material. It is important to calculate the load on foundationbearing structures and roof so that the integrity of the structure is not violated.
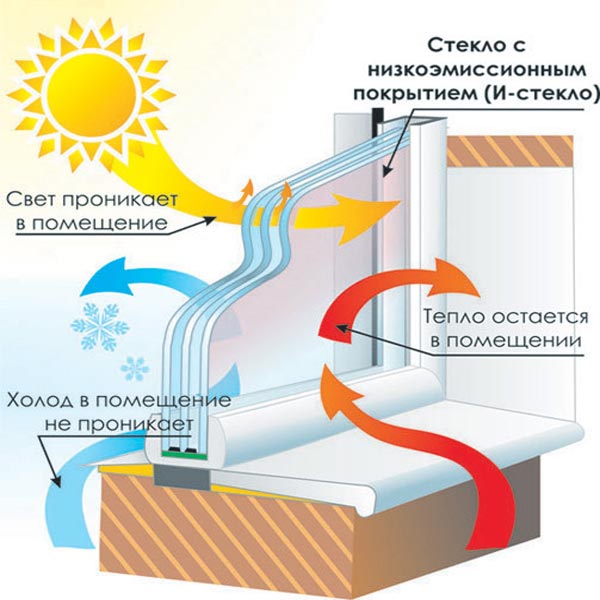
Thermal insulation of window openings
The windows account for 20% of the heat loss at home. Though modern double-glazed windows better than old wooden windows, protect the house from drafts and isolate the room from external influences, they are not ideal.
More advanced options for an energy-efficient home are:
- selective glassesthat work on the principle of the earth's atmosphere. They let in shortwave radiation, but they didn’t let out heat rays, creating a “greenhouse effect”. Selective glasses are I- and K-type. On the And glass the coating is applied in a vacuum to the finished material. On the K-glass the coating is applied during the manufacturing process using a chemical reaction. I-glasses are considered more effective, since they retain 90% of the heat, while K-glasses - 70%;

- inert gas selective glasses minimize heat loss through windows. The thermal conductivity of the inert gas used is lower than that of air, so the house almost does not lose heat through them.
Thermal insulation of the floor and foundation
Through the foundation and the floor of the first floor, 10% of the heat is lost. The floor is insulated with the same materials as the walls, but other options can be used: bulk heat-insulating mixes, foam concrete and aerated concrete, granulobeton with a record thermal conductivity of 0.1 W / (m ° C). It is possible to insulate not the floor, but the basement ceiling, if such is provided for by the project.
It is better to insulate the foundation from the outside, which will help protect it not only from freezing, but also from other negative factors, including the effects of groundwater, temperature extremes, etc. In order to warm the foundation use sprayed polyurethane, expanded clay and polystyrene.
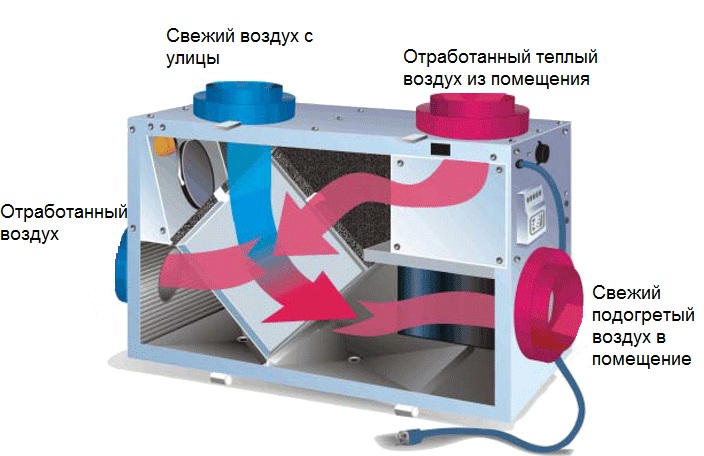
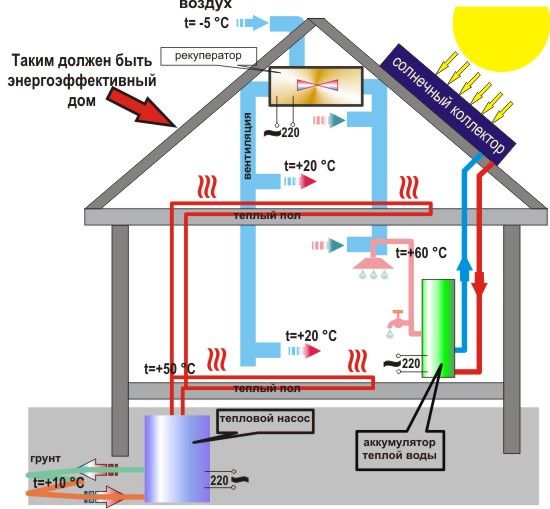
Number 4. Heat recovery
The heat from the house leaves not only through the walls and roof, but also through ventilation system. In order to reduce heating costs, supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery is used.
Recuperator called a heat exchanger, which is built into the ventilation system. The principle of its work is as follows. Heated air through the ventilation ducts leaves the room, gives its heat to the heat exchanger in contact with it. Cold fresh air from the street, passing through the recuperator, heats up, and enters the house at room temperature. As a result, households get clean fresh air, but do not lose heat.
A similar ventilation system can be used together with natural ventilation: air will enter the room forcibly, and will come out due to natural draft. There is one more trick. An air intake cabinet can be 10 meters from the house, and air duct laid underground at freezing depth. In this case, even before the recuperator, in the summer the air will be cooled, and in the winter it will be heated due to soil temperature.
No. 5. Smart House
To make life more comfortable while saving resources, you can furnish the house smart systems and technologythanks to which it is already possible today:
- set the temperature in each room;
- automatically lower the temperature in the room if no one is in it;
- turn on and off the light depending on the presence of a person in the room;
- adjust the light level;
- automatically turn on and off ventilation depending on the air condition;
- automatically open and close windows for the entry of cold or warm air into the house;
- automatically open and close jalousie to create the required level of lighting in the room.

No. 6. Heating and hot water supply
Solar systems
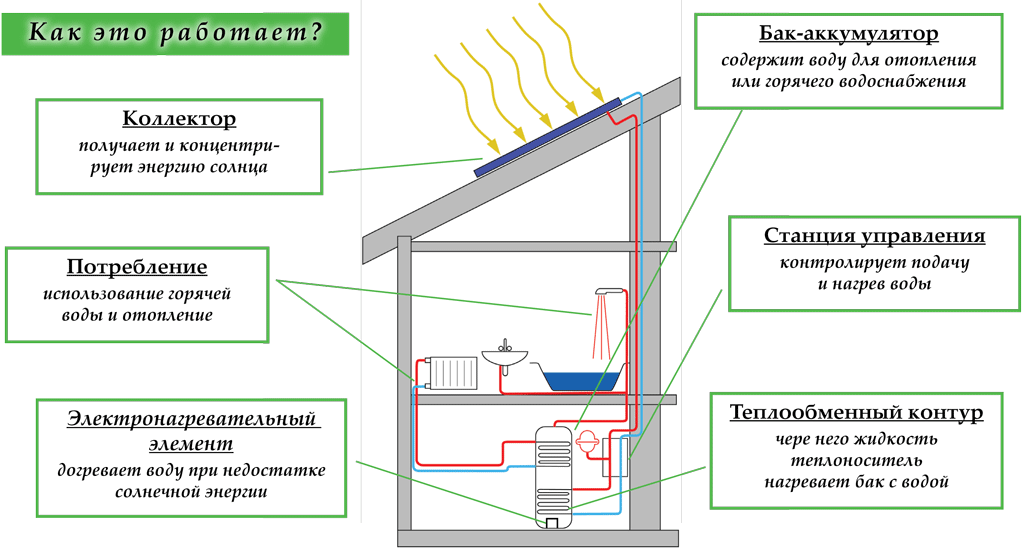
The most economical and environmentally friendly way to heat a room and heat water - This is to use the energy of the sun. Perhaps this is due to solar collectors installed on the roof of the house. Such devices are easily connected to the heating system and hot water supply of the house, and the principle of their work is as follows. The system consists of the collector itself, the heat exchange circuit, the storage tank and the control station.A coolant (liquid) circulates in the collector, which is heated by the energy of the sun and transfers heat through the heat exchanger to the water in the storage tank. The latter, due to good thermal insulation, is able to retain hot water for a long time. In this system, a backup heater can be installed, which heats the water to the required temperature in case of cloudy weather or insufficient duration of sunshine.
Collectors can be flat and vacuum. Flat ones are a box covered with glass, inside it is a layer with tubes through which the coolant circulates. Such collectors are more durable, but today they are superseded by vacuum ones. The latter consist of many tubes, inside which are still a tube or several with a coolant. Between the outer and inner tubes is a vacuum that serves as a heat insulator. Vacuum collectors are more efficient, even in winter and in cloudy weather, maintainable. The service life of the collectors is about 30 years or more.
Heat pumps
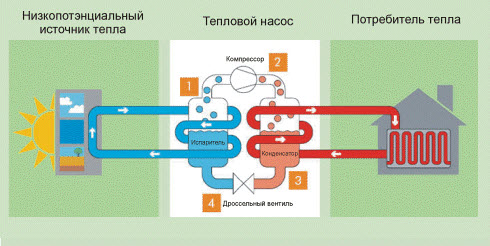
Heat pumps use low-potential heat of the environment for heating a houseincluding air, bowels and even secondary heat, for example from the central heating pipeline. Such devices consist of an evaporator, a condenser, an expansion valve and a compressor. All of them are connected by a closed pipeline and operate on the basis of the Carnot principle. Simply put, a heat pump is similar in operation to a refrigerator, only it works the other way around. If in the 80s of the last century heat pumps were a rarity and even a luxury, then today in Sweden, for example, 70% of houses are heated in this way.
Condensing boilers
Ordinary gas boilers They work according to a rather simple principle and consume a lot of fuel. In traditional gas boilers after burning the gas and heating the heat exchanger, the flue gases escape into chimneyalthough they carry a fairly high potential. Condensing boilers due to a second heat exchanger heat is removed from the condensed air vapor, due to which the efficiency of the installation can exceed even 100%, which fits into the concept of an energy-saving house.
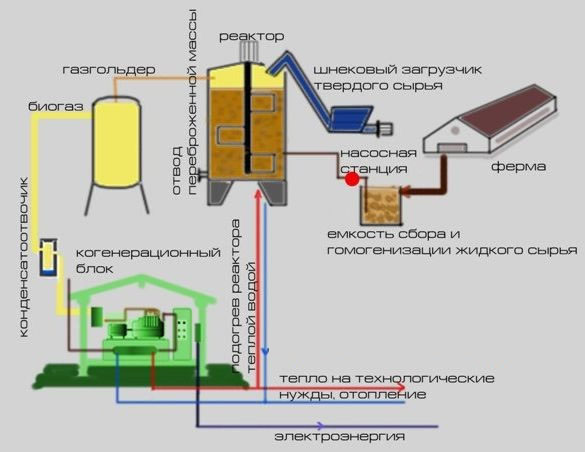
Biogas as a fuel
If a lot of organic agricultural waste accumulates, then you can build bioreactor for biogas production. Thanks to anaerobic bacteria, biomass is processed in it, resulting in the formation of biogas, which consists of 60% methane, 35% carbon dioxide and 5% of other impurities. After the cleaning process, it can be used for heating and domestic hot water. Recycled waste is converted into excellent fertilizer that can be used in the fields.
Number 7. Power sources
Energy-saving home should use electricity as economically as possible and, preferably, get it from renewable sources. To date, a lot of technologies have been implemented for this.
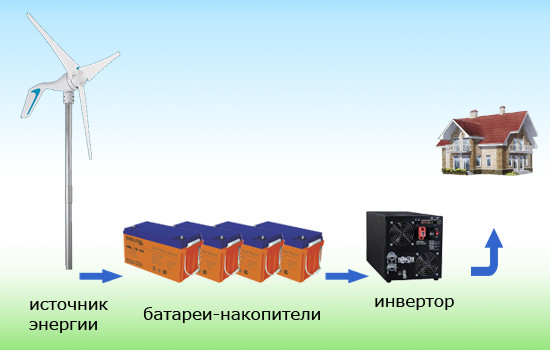
Wind generator
Wind energy can be converted into electricity not only by large wind turbines, but also by compact "home" windmills. In windy areas, such installations are able to fully provide electricity to a small house, in regions with a low wind speed they are best used with solar panels.
The force of the wind drives the blades of the windmill, which make the rotor of the electric power generator rotate. The generator generates an alternating unstable current, which is rectified in the controller. There, batteries are charged, which, in turn, are connected to inverters, where the DC voltage is converted to alternating voltage used by the consumer.
Windmills can be with a horizontal and vertical axis of rotation. At a one-time cost, they permanently solve the problem of non-volatility.
Solar battery
The use of sunlight to generate electricity is not so common, but in the near future the situation risks changing dramatically. The principle of operation of the solar battery very simple: a pn junction is used to convert sunlight to electricity. The directional movement of electrons provoked by solar energy is electricity.
The designs and materials used are constantly being improved, and the amount of electricity directly depends on the lighting. While the most popular are various modifications silicon solar cells, but an alternative to them are new polymer film batteries, which are still under development.
Energy saving
Received electricity must be able to spend wisely. The following solutions are useful for this:
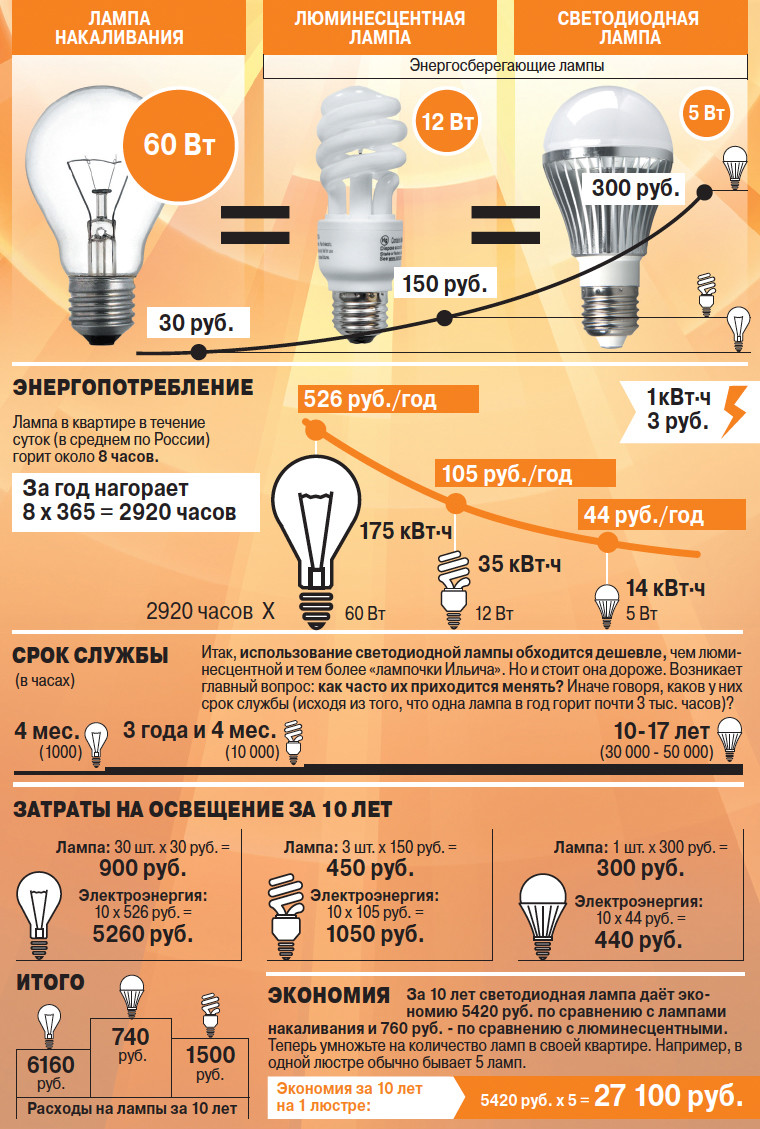
- using led bulbswhich are two times more economical than luminescent and almost 10 times more economical than ordinary "Ilyich bulbs";

- using energy saving technology class A, A +, A ++, etc. Although initially it is slightly more expensive than the same devices with higher power consumption, in the future the savings will be significant;
- use of presence sensorsso that the light in the rooms does not burn in vain, and other smart systems, which were mentioned above;
- if you had to use electricity for heating, then ordinary radiators are better to replace with more advanced systems. it thermal panelswhich consume half the electric power than traditional systems, which is achieved through the use of heat-accumulating coatings. Similar savings are provided and monolithic quartz moduleswhose operating principle is based on the ability of quartz sand to accumulate and retain heat. Another option is film radiant electric heaters. They are mounted on the ceiling, and infrared radiation heats the floor and objects in the room, thereby achieving the optimal microclimate of the room and saving electricity.
Number 8. Water supply and sewerage
Ideally, an energy-efficient home should receive water from a welllocated under the dwelling. But when the water lies at great depths or its quality does not meet the requirements, such a decision has to be abandoned.
It is better to pass household drains through a recuperator and take away their warmth. For wastewater treatment, you can use septic tankwhere the conversion will occur through anaerobic bacteria. The resulting compost is a good fertilizer.
To save water, it would be nice to reduce the volume of drained water. In addition, the system can be implemented when the water used in the bathroom and the sink is used to flush the toilet.
No. 9. What to build an energy-saving house
Of course, it is better to use the most natural and natural raw materials, the production of which does not require numerous processing stages. it wood and stone. It is better to give preference to materials that are produced in the region, because in this way transport costs are reduced. In Europe, passive houses began to be built from inorganic waste products. It's concrete, glass and metal.
If once you pay attention to the study of energy-saving technologies, think over the project of the eco-house and invest in it, in subsequent years the cost of its maintenance will be minimal or even tend to zero.
















Why did not describe new technologies from solarcity?
The author urgently needs the Nobel Prize for "the efficiency of the installation can exceed even 100%"
Igor, thanks for your ironic comment and attention to the article. We advise you to understand the material a little deeper. The efficiency of a condensing boiler can exceed 100%, since the heat is withdrawn not only from burning fuel, but also from flue gases. In passports for condensing boilers, the efficiency is about 107-109%. Of course, one can argue about the methods of calculation, but the generally accepted technique is taken as the basis, according to which the efficiency of the boiler is considered as the ratio of the amount of heat transferred to water to the amount of heat received during fuel combustion. Those 11% of the heat that is spent on evaporating moisture is simply discarded in this technique. When it comes to condensing boilers, these 11% are added (it is clear from the principle of operation) and 2-4% are deductible for losses, so the final efficiency is 107-109%. The technique is not perfect - there are claims to it, but we are not scientists to use our own methods of calculation in the articles.
interesting article, thanks to the author