Options for sewer pipes for digging into the ground
In this article we will help you figure out which trumpet better for sewers underground, consider the advantages and disadvantages of various materials, the required diameter and connection options.
What pipe to use for sewage underground
 The market offers to our attention pipes for underground sewers of various diameters, materials and connection options.
The market offers to our attention pipes for underground sewers of various diameters, materials and connection options.
To make a competent choice, you must consider:
- temperature and chemical aggressiveness of effluents;
- discharges during periods of maximum load;
- minimum temperatures of the climatic zone;
- depth and angle of sewage;
- type of soil.
Outdoor sewer pipes must meet multiple requirements: to be strong, reliable, wear-resistant and frost resistant. Correctly selected sewer pipes for specific conditions will ensure effective drainage for many years.
Pipe material
Underground sewage can be laid using the following materials:
- cast iron;
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- polypropylene (PP);
- polyethylene (PE);
- asbestos cement;
- ceramics.
The last two options are used very rarely, and more and more users opt for pipes made of cast iron and plastic.
Cast iron pipes
Gray cast iron is inferior in its characteristics to malleable cast iron. In the modern version, cast-iron socketless pipes sml are recommended.
Advantages:
- durable;
- service life up to 85 years;
- withstand heavy loads;
- resistance to temperature differences.
Disadvantages:
- not suitable for solonchak soil;
- they are heavy, increasing the cost of delivery and complicating the installation process;
- rough surface reduces the flow rate of drains and provokes blockages;
- high price.
PVC pipes
PVC pipesintended for external use, produced in orange. Gray have a wall thickness of 2.7 mm and are not able to withstand the pressure of the soil, therefore, they are used for installation exclusively of internal sewers. Corrugated pipes are intended for laying in the ground without boxes to a depth of more than two meters.
Advantages:
- affordable price;
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- strength, wear resistance;
- do not collapse under the influence of aggressive chemistry;
- the inner walls are smooth, so no growths form on them;
- light weight, which facilitates installation;
- corrosion resistance.
Disadvantages:
- if the temperature of the effluent is above 40 ° C, they quickly become worthless due to the temperature elongation of the material;
- only suitable for gravity drainage;
- apply to small private houses.
It is also worth noting that the characteristics of PVC pipes may vary depending on the manufacturer. In addition, such pipes may vary in stiffness, and depending on it, be used at different depths. The toughest grade S pipes can be used at depths of up to 8 m, medium hard grade N pipes can be used at depths of up to 6 m, and lightweight class L pipes can be used at depths of up to 2 m.
Polypropylene pipes
Advantages:
- smooth inner surface;
- service life up to 100 years;
- resistant to temperatures up to 100 ° C;
- do not decompose under the influence of acids and alkalis;
- light weight, which simplifies transportation and installation;
- installation is quite simple and quick, does not require the use of special equipment.
Disadvantages:
- soft, can deform under high pressure;
- pipes with increased wall thickness, designed for digging to a greater depth, are more expensive;
- deteriorate under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, which complicates storage.
Polyethylene pipes
On sale there are smooth and corrugated, with greater strength.
Advantages:
- resistance to loads allows laying pipes from PP to a depth of 15 m;
- smooth surface with high throughput;
- a light weight;
- on sale a wide range of connectors, tees and bends that facilitate the installation process;
- the service life exceeds 50 years.
Disadvantages:
- can not be used for drains with temperatures above 65 ° C;
- deteriorate from UV radiation;
- can only be laid in the ground, it is unacceptable for a part of the system to exit over the ground.
With a huge number of advantages, plastic has low strength, so the outer surface of the pipes is corrugated, increasing their rigidity. The inner surface remains smooth so as not to trap drains.
Asbestos cement
For the production of such pipes, a mixture of Portland cement and asbestos fiber is used.
Advantages:
- excellent resistance to aggressive environments, therefore, virtually any effluent can be drained through such pipes;
- durability, and in this regard, asbestos-cement pipes are in the lead, as they can be operated up to 100 years;
- simplicity of laying, since it is quite simple to dock individual parts of pipes;
- light weight, which facilitates installation;
- such pipes are not prone to overgrowth, so for many years they will serve as they should.
Disadvantages:
- high brittleness, since even slight mechanical damage can violate the integrity of the material. Even new pipes at the ends can have chips and cracks, so when buying, you need to carefully look at them;
- delivery complexity due to high fragility.
These shortcomings cross out all the advantages of asbestos-cement pipes, so they are practically not used today.
Ceramics
Ceramics have been used for the production of sewer pipes since antiquity, and today this material is still used for these purposes.
Advantages:
- high resistance to temperature extremes, extremely low and high temperatures;
- complete inertness to any substances, even strong alkalis, even acids. Such pipes can withstand the influence of absolutely any effluent;
- ease of installation;
- the inner surface is characterized by low roughness, which means that it will not overgrow and become clogged.
Disadvantages:
- too high brittleness, which complicates the transportation of pipes and their installation. New pipes may already have cracks, and their presence is indicated by a slightly rattling sound when tapped on the pipe;
- ceramic pipes do not differ in great length, which leads to the need to make a large number of joints, and this negatively affects the integrity of the system;
It is because of the high fragility that using ceramic pipes is very difficult, and they are almost crowded out of the modern market.
Diameter
Choosing the diameter of the sewer pipe, it is necessary to take into account the external and internal dimensions, since the wall thickness can vary significantly.
For household outdoor sewage applicable standard 110 mm. This diameter is enough for maintenance country house. When combining several houses or a whole village into one sewer network, the diameter should increase in accordance with the project calculations.
All the time it was a question of pipes with a circular cross-section, which are used in the vast majority of cases, because the drains move through them as quickly as possible. However, this is far from the only option. Sometimes used elliptical tubes: they are necessary when the soil creates strong pressure on the pipes or when the load on the pipes is too high. When the sewage system is not too deep (up to 1 m), pipes with a semicircular and rectangular section can be used. It is also worth noting that if the sewer system is not deep enough, it is necessary to isolate it to avoid pipe rupture in the cold season.
Connection Format
- Welding- the most complex, requiring special knowledge and application of equipment. Welding is performed on metal and plastic pipes. Such connections are extremely inconvenient in cases of need for repair.
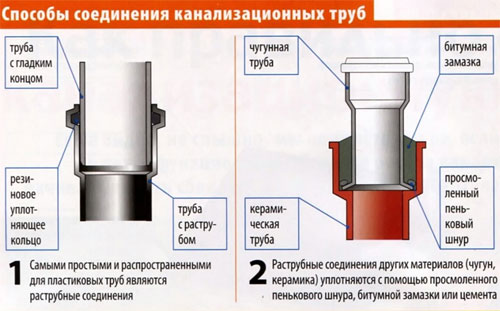
- Bell-shaped - a slice of one pipe is installed in the socket of another. Joint tightness is achieved through the use of rubber seals and sealants. When using this method, the installation of cast iron pipes additionally makes caulking tow.
- Bellless (flange, coupling) - pipes, straight from both ends, are joined butt-to-butt, a rubber cuff is applied to the connection and tightened with a hose clamp. The socketless method of connections is most convenient for repairs and replacements of the sewer section.
By analyzing which underground sewer pipes are most suitable in a particular case, you will get rid of many problems associated with the difficulties of cleaning and repair.