11 tips for insulating a water pipe
Quality insulation water pipes is the key to the durability and uninterrupted operation of the system. Is this not one of the essential components of a comfortable stay in a private or country house? One way to protect pipes from freezing is laying them to a depth that is at least 10 cm greater than the freezing depth of the soil in your area. However, given the fact that in some places the soil may be swampy due to the high level of groundwater, it is simply not possible to perform such deep laying. The maximum by which it is possible to actually deepen the water supply system under such conditions is 50-80 cm. In this case, it is recommended to perform warming regardless of belonging to a particular climatic zone. Let's try to figure it outhow and how to insulate a water pipewhich material is better to choose and what requirements a high-quality insulation should meet.
1. The main types of thermal insulation
I would immediately like to note that the most effective will be timely warming, which is best done right at the time of laying the pipeline. Many consider deepening pipes to a decent depth as a sufficient measure.
- However, as we have already said, this is not always possible because of the characteristics of the soil.
- Secondly, if the work is planned to be carried out independently, then you will inevitably encounter a very long and laborious process. It is advisable to dig deep trenches if you have special equipment at your disposal to facilitate this task.
- Well, and thirdly, if you are faced with the need to perform local repairs or replace the damaged pipe segment, this will be problematic due to the large depth.
 Doing without insulation, especially now when the range of thermal insulation materials is so wide, and simply relying on the climate to be favorable to you is a rather rash decision. After all, it’s hard not to notice that recently the weather has brought us surprises in the form of abnormal frosts or, conversely, abnormal heat. Depending on the type of materials used, isolation methods can be divided into three types:
Doing without insulation, especially now when the range of thermal insulation materials is so wide, and simply relying on the climate to be favorable to you is a rather rash decision. After all, it’s hard not to notice that recently the weather has brought us surprises in the form of abnormal frosts or, conversely, abnormal heat. Depending on the type of materials used, isolation methods can be divided into three types:
- Reflective - when materials with an additional foil or aluminum layer are used for insulation, which reflect the cold from the environment and do not allow it to affect the surface of the pipe;
- Loss prevention heat - we are talking about materials that have a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, water and vapor permeability;
- Heating - when more modern methods are used, for example, heating cable. In this case, the insulation occurs due to the heat generated by the heater. In order to minimize heat loss and direct it to the heated pipe as much as possible, it is additionally recommended to perform insulation with materials with a foil layer.

2. Requirements for thermal insulation materials
Whatever type of insulation you choose, you still have to face the need to choose the right material. First you need to decide what qualities must have a heat insulating material that can really provide the desired result.
- The most important parameter is its value thermal conductivity coefficient. The lower this value, the better thermal insulation will come out;
- If we are talking about warming the most vulnerable sections of the pipeline, namely those that pass in the open ground, it is necessary to select materials with high density and deformation resistance. The soil layer exerts significant pressure on the surface of the pipe, and therefore the insulation. Moreover, the indicator of pressure can vary depending on the amount and frequency of precipitation, average temperature and other indicators;
- An important condition is the increased moisture resistance. Under the influence of moisture, which may be in excess in the surrounding soil, many heaters lose their insulating properties;
- Also, moisture in the soil can have a detrimental effect on the surface of the pipes, which over time will manifest as corrosion. Thermal insulation material, in addition to protection against freezing, additionally acts as protection against this undesirable phenomenon. Therefore, its structure should be corrosion resistant;

- For plastic plumbing is very important Fire safety, it means that the insulation must be fireproof;
- The material must withstand the effects of high temperatures and not undergo a change with sudden changes in temperature;
- For economic benefits, it is better to choose a heater that can be reused;
- The determining factor is and material durability. Not always to acquire cheaper material in the future will be cost-effective. It is better to spend a slightly larger amount and provide reliable insulation that will last several decades than to make regular replacement of the insulation simply because it has lost its properties. Not to mention the fact that for this it will be necessary to dig trenches, and then bury them again.
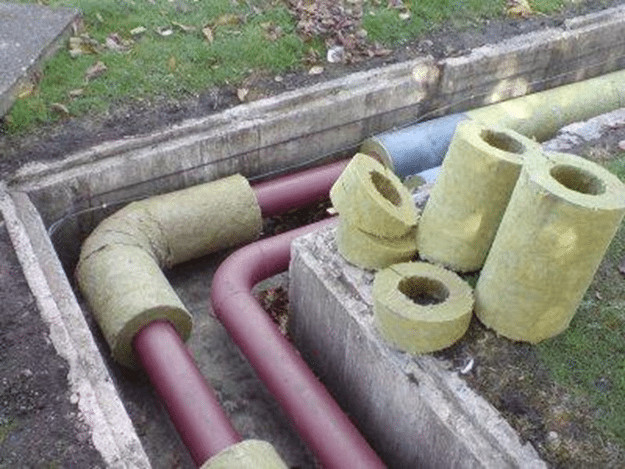
3. Mineral wool
Thermal insulation using varieties of mineral wool has become enormous thanks to its affordable cost. With its help you can warm heating pipes, hot water, tap and sewer systems, and air ducts. This material works on the principle of a thermos. In addition, cotton wool protects the surface of pipes from condensation. In case of warming the underground pipeline, it is imperative to provide additional protection against moisture, so when wet, the cotton wool loses its protective properties, and heat loss, in turn, increases. Mineral wool is a fibrous material for the manufacture of which different raw materials are used. The most commonly used varieties are:
- Glass wool - made from the same raw materials used for the manufacture of glass. Its fibers are quite thick. For convenience, glass wool is available in the form of plates, in rolls or in the form of shells. To protect against moisture, one side can be covered with foil or a thin layer of aluminum. The coefficient of thermal conductivity is 0.030-0.052 W / m * K. The material belongs to the class of NG - non-combustible. When installing glass wool, you must be extremely careful and take care of personal protective equipment. Since with any touch to the material, small sharp particles fly apart in different directions, which stick into the skin even through fabric gloves. It is especially important to protect the organs of vision and breathing, since getting into the lungs, the particles cause their strong and prolonged swelling;

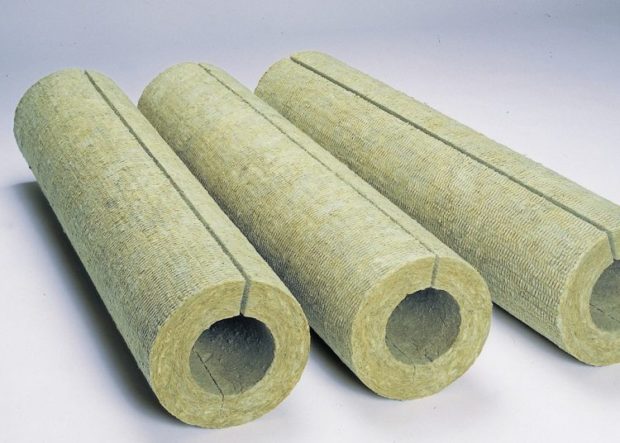
- Basalt Vata - made from molten rocks. It is superior in weight to glass wool. The material is also non-combustible and able to withstand very high temperatures - up to 870 ° C. The thermal conductivity index is lower than that of the previous variety and amounts to 0.035-0.039 W / m * K.Stone wool has a higher density and hardness. In this regard, the form of release can be either in the form of plates, or in the form of cylinders. An additional foil layer can be implemented on both forms;

- Slag wool - made from waste after the production of cast iron. For pipe insulation, it is used quite rarely. This is due to the increased friability and acidity of the material, on the surface of which over time, oxides are formed that adversely affect the surface of the pipes. In addition, the material can not be classified as environmentally friendly. And the coefficient of its thermal conductivity is quite high as for a heat-insulating material - 0.46-0.48 W / m * K.

4. Polyfoam
This material is quite effective insulation, which has a small weight. This greatly facilitates the process of installation. Due to sufficient rigidity and strength, the foam does not deform under the pressure of the soil. The main form of release pipe foam insulation are cylinders. They consist of two halves, which are interconnected by means of a tenon groove. This is not only very convenient, but also completely eliminates the possibility of the formation of cold bridges. Most common varieties of foam are:
This is not only very convenient, but also completely eliminates the possibility of the formation of cold bridges. Most common varieties of foam are:
- Penoizol;
- Extruded polystyrene foam;
- Expanded polystyrene foam.
The above materials are distinguished by their density. Depending on this, the thickness of the insulating layer also changes, which can lie in the range from 20 to 100 mm or more. The inner diameters of the foam cylinders are equal to the standard outer diameters of the water pipes, which allows them to be insulated provided that they fall into the diameter range from 15 to 144 mm. The coefficient of working temperatures of the material is also sufficient - from -188 to + 95 ° С. Foam Shells often used for noise and heat insulation not only of water supply, but also ventilation and air conditioning systems, sewers and gas pipelines. Having chosen one of the varieties of foam as a heater, you can count on the following advantages:
- Minimal heat loss;
- Pipe corrosion protection;
- Tightness of a heat-insulating layer;
- Possibility of reusable connection;
- The ability to use the shell as an additional insulation when warming with a heating cable. Since there are varieties of cylinders with a special groove for cable laying;

- Resistance to the chemical effects of salts, lime and acids that may be in the soil and also to the vital processes of various microorganisms;
- Durability;
- Resistance to sudden changes in temperature;
- An opportunity to pick up a protective shell even for fitting connections thanks to existence of shaped details.

Among disadvantages hypersensitivity to such solvents as gasoline, acetone, nitro-paint can be noted. Under their action, the material simply melts.
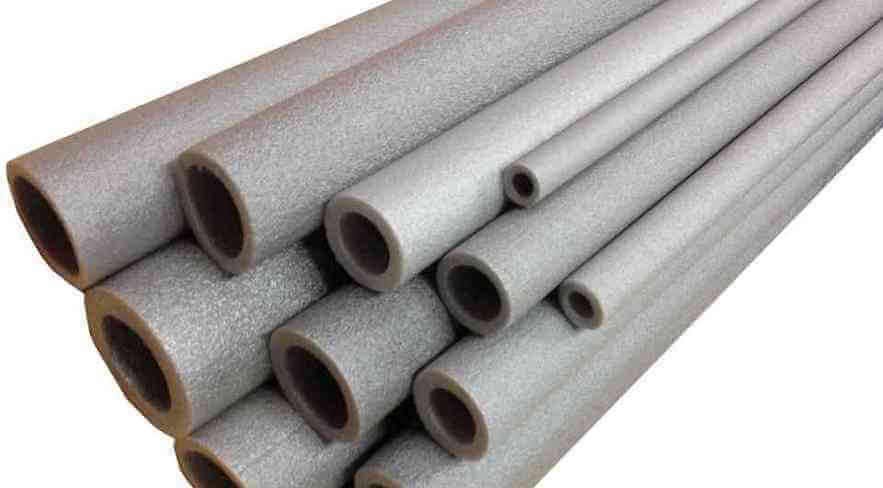
5. Foamed polyethylene
Many experts note that among the whole variety of heat-insulating materials, namely polyethylene varieties are the most optimal in terms of price / quality. The structure of polyethylene consists of many closed cells, inside of which there is air, which, as you know, has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient - only 0.024 W / m * K. Distinguish:
- stitched (PPPE or KhPPE) polyethylene foam, which is obtained by foaming the molten composition;
- uncrosslinked (NPE) polyethylene foam, for the manufacture of which an extruder is used.
The structure of NPEs is long linear molecules between which there is no chemical bond. While cross-linked polyethylene has a denser structure consisting of smaller cells, with a stable molecular bond. You can distinguish these two varieties even visually. 
Depending on the production method differ and technical specifications material.
- Crosslinked polyethylene will have a lower coefficient of thermal conductivity and higher density, which makes it resistant to deformation. But its cost will be much higher than uncrosslinked. Density ranges from 25 to 40 kg / m3;
- The material has increased elasticity, which remains even at low temperatures (-80 ° C). This greatly facilitates installation;
- With a force of 5000 N / m.sq. the compression ratio of polyethylene is only 0.2;
- Due to the minimum value of the vapor permeability coefficient, which is 0.001 mg / m * h * Pa, the material can be classified as completely vapor-tight;
- The coefficient of thermal conductivity is 0.035 W / m * K;

- Also, polyethylene has a low rate of water absorption. When the material is immersed in water for a day, it absorbs no more than 0.5% moisture from its volume. Moreover, upon reaching the indicator of 1.9% after more time, water absorption ceases to increase;
- The combustibility class of the material is G2 (moderately flammable);
- Moreover, in case of ignition, the material does not emit substances harmful to the body;
- The structure of the material is not susceptible to the effects of various chemical elements.
- Polyethylene can be in the form of an outlet in the form of hollow cylinders with a technical slot along the entire length, sheets and rolls. The material may have an additional protective layer of foil.

6. Polyurethane foam (PPU)
This material is no less effective insulation. For pipe insulation shell of PPU, which is a cylinder. It is made in two ways:
- Liquid Fill Method polyurethane under high pressure in a special mold:
- Pipe-to-pipe manufacturing. In this case, the material is poured into the cavity between the two pipes - an inner one, with a smaller diameter and an outer one, with a larger diameter.
The first option is suitable for warming an independent pipeline. And the product of the second production method is ready for laying a new pipeline pipes pre-insulated. 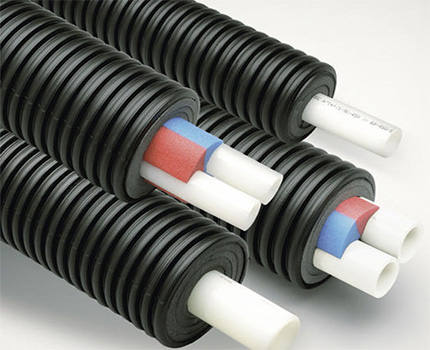
- This is a completely new product, which makes it possible not to think about additional isolation;
- In this case, the outer layer can be corrugated - flexible, which makes it possible to avoid the need to use rotary fittings, that is, the pipeline can be laid with a minimum number of connections;
- Both single and double pipe versions of such finished elements are produced;
- For laying a cold pipeline, constructions with plastic pipes are better;

- For hot produce more expensive options with metal pipes inside;
- Pre-insulated flexible pipes are supplied in bays and are up to 200 meters long.
Regarding shell of PPU, she has the following advantages:
- Heat loss is reduced by almost 40%;
- Installation of elements is so simple that it allows you to independently insulate several hundred meters of the pipeline per day;
- This indicates the installation speed;
- The material is environmentally friendly;
- The insulation can be reused an unlimited number of times;
- The service life reaches 30 years.


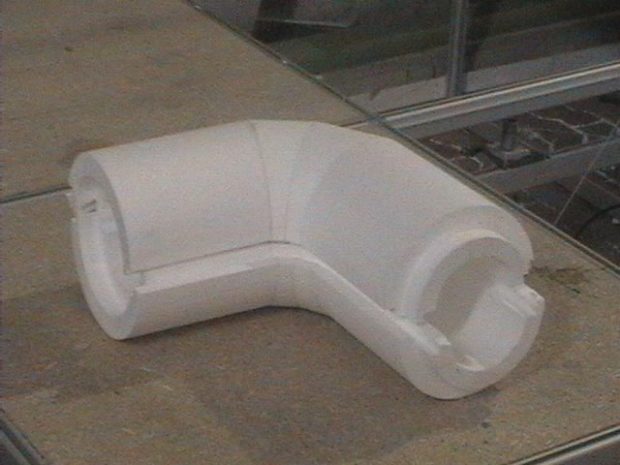
Among disadvantages note the impossibility of using the material at temperatures above 120 ° C. Great convenience is the presence of shaped segments, such as tees, bends and branches. The connection of two fragments of the shell with each other occurs using a special coupling, which makes the insulation tight and does not allow the formation of cold bridges. Also shell differs and by material outdoor coverings which determines the scope of its application. The coating can protect both from the effects of environmental factors, such as ultraviolet radiation, and from mechanical influences.
Also shell differs and by material outdoor coverings which determines the scope of its application. The coating can protect both from the effects of environmental factors, such as ultraviolet radiation, and from mechanical influences.
- PPU without coating - is the most affordable, but can only be used for insulation of pipes located, for example, in the basement and then subject to the availability of an additional casing. Or as an intermediate insulation layer;

- Foil-coated shell - the scope is not limited, and the material is characterized by increased strength;

- A shell with a coating of their fiberglass can be used to warm the outer sections of the pipeline, for example, places of the pipe plant in the house. It is distinguished by its resistance to ultraviolet light. At the same time, fiberglass is also characterized by high hardness, which virtually eliminates the possibility of mechanical damage;

- The glassine coating is resistant to direct sunlight, but inferior to fiberglass in strength;

- Shell with a coating of reinforced aluminum foil (armofol) - is used to warm the pipeline, operated in conditions of significant temperature extremes;

- Galvanized steel coating is used for insulation of pipelines passing in the air. Steel protects the shell from ultraviolet radiation, mechanical and biological influences, but at the same time it is more affordable than a fiberglass coating.

Shell thickness is 20-80 mm and increases with increasing diameter. Length one element does not exceed 1000 meters given the features of the manufacturing process.
7. Foamed synthetic rubber
This material is made from natural or synthetic rubber and is classified as a material with increased elasticity. At the same time, high tear resistance is maintained. The rubber structure consists of 90% closed cells. This allowed us to achieve such positive characteristics:
- The coefficient of thermal conductivity is 0.024-0.038 W / m * K and directly depends on the ambient temperature. The largest indicator is observed at 0 ... + 20 ° C;
- The material has excellent anti-corrosion properties;
- It is resistant to substances such as gasoline and oil;
- It has a low coefficient of water absorption and vapor permeability;
- The range of operating temperatures is quite wide - from -200 to + 150 ° C;
- In the conditions of sharp temperature changes, it retains its properties unchanged;
- In addition to reliable thermal insulation, it also provides high noise insulation;
- Has the ability to reuse;
- It is durable;
- Can be reused.
Release form foam rubber - sheets or hollow cylinders with a technical slot equipped with an adhesive layer. The thickness of the insulation is 6-32 mm, and the inner diameter is designed for pipes with a diameter of 6 to 114 mm.
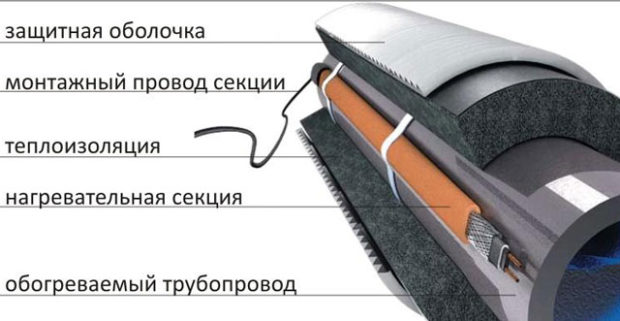
8. Heating cable
One of the most effective ways to provide long-term protection of pipes against freezing is to use a heating cable. Advantage This solution is that installation can be done both on top of the pipe and inside it. It all depends on the condition of the pipeline and the diameter of the pipes. When choosing an internal installation method, keep in mind that the cable can reduce pipe throughput if its diameter is too small. The recommended minimum pipe inner diameter is 40 mm. The heating cable itself can be of two types:
- Resistive
- Self-regulating.
The latter type is more perfect, convenient and cost-effective. Its cost exceeds the cost of a resistive cable.  However, given the fact that the finished heating system can almost completely do without human intervention and requires minimal attention, it can be argued that the costs are justified. More Full description You can find both types of heating cable and the features of its selection and installation in our article by going to this link.
However, given the fact that the finished heating system can almost completely do without human intervention and requires minimal attention, it can be argued that the costs are justified. More Full description You can find both types of heating cable and the features of its selection and installation in our article by going to this link.
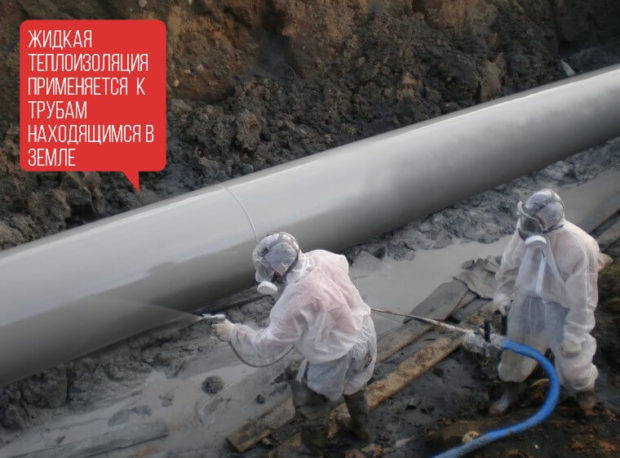
9. Liquid insulation
A completely new way of warming is the use of special coloring compounds. Even a thin layer of similar paint can replace by myself isolation 10-20 mm thick. And if you apply the composition in several layers, you can achieve much better results. Heat loss can be reduced to 40% while the coating does not allow water and moisture to pass through, but remains “breathable”. Liquid insulation is classified as energy saving heat paint and can have two varieties:
- Ceramic, in its consistency, really reminiscent of ordinary paint;
- In the form of a foam structure, which is applied to the desired surface by spraying.

The coating works on the principle of a thermos. The layer of material required for thermal insulation is very thin - only 0.5 mm. TO the benefits this method of insulation include:
- When using the composition in the form of paint, applying it is quite simple and can be done with an ordinary brush;
- If the coating is chipped or scratched, it is easy to repair;
- Low coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- High elasticity, which allows the coating not to crack when expanding and narrowing the diameter of the pipes;
- Long term of operation;
- Health safety;
- Condensation and corrosion do not form on the surface;
- Possibility of applying to the surface of any configuration.

TO disadvantages include:
- The high cost of the composition;
- If you choose a foam composition as a heater, for its application you will need to seek the help of specialists. Which, as you know, provide their services only with large volumes of work. If you want to spray just a few meters of the pipeline, then you simply can’t find an artist.
10. Thermal insulation using high pressure
As a method of warming the pipeline in a private house or in the country, you can consider creating and maintaining high pressure in it. How it's done:
- It is necessary to embed a receiver into the finished pipeline, which will have to create the necessary pressure - 3-5 atmospheres is enough;
- It is also necessary to additionally use a submersible pump to create a pressure of 5 to 7 atm .;

- After the pump, the check valve and tap are installed in front of the receiver;
- To start the system, close the tap in front of the receiver and turn on the pump;
- The resulting pressure must be maintained in the system continuously until it is in operation;
- To enable the pipeline to function again, you just need to vent excess air.
11. Air insulation
Understanding the features of soil freezing in winter, we can apply the method of thermal insulation, when it will be used to heat the pipe warm air and bowels land. As you know, the soil freezes from top to bottom, while the bottom continues to receive heat at this time. When insulating shells are used, this heat is simply cut off and not used.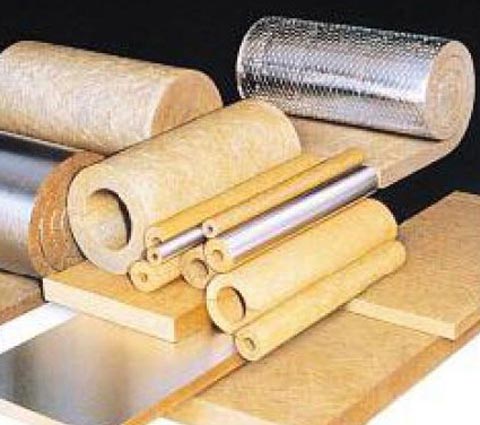 To a little to save on the amount of insulation materials, you can create a design that will resemble an umbrella. And work on the same principle. The cold from above will be insulated, and the heat coming from below will be concentrated at the depth of the pipeline. This can be done using a flexible material with low thermal conductivity, which is laid by an arc over the pipe in a trench, and then simply covered with soil. Additionally, you can fill up more free space around the pipe expanded clay.
To a little to save on the amount of insulation materials, you can create a design that will resemble an umbrella. And work on the same principle. The cold from above will be insulated, and the heat coming from below will be concentrated at the depth of the pipeline. This can be done using a flexible material with low thermal conductivity, which is laid by an arc over the pipe in a trench, and then simply covered with soil. Additionally, you can fill up more free space around the pipe expanded clay.